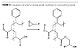
Trimethylol Propane Monoallyl Ether as Hydroxyl-Functional Co-Monomer

Hydroxyl Functionalization of Acrylic Backbones
Another approach is functionalization of the acrylic backbone, in most cases acid functional, to a hydroxyl-functional one, in which case the hydroxyl functionality is a secondary group (Figure 1).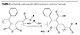
The approach allows a larger latitude of formulation, targeting a lower or higher mobility of the hydroxyl group, related to the length of the R’ chain. In most cases propylene glycol, ethylene glycol, 1,6-hexane diol and 1,4-butane diol may be used but also cyclohexane dimethanol, 1,4- or a commercial blend with the 1,3- isomer. However the limitation of the method resides in the risk for looping and interchain esterification that may lead to gellation. This approach also increases the acid functionality at the same rate as the hydroxyl functionality.
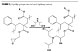

Trimethylol Propane Monoallyl Ether as Hydroxyl-Functional Co-Monomer
The present work introduces a new hydroxyl-functional monomer having the benefits of lower equivalent weight, higher flexibility, lower viscosity due to aliphatic substituent, and the same mobility and reactivity of the hydroxyl groups. The monomer is trimethylol propane monoallyl ether, or TMPME (Figure 4).Although the allyl group may show lower reactivity in the polymerization process, no experiment in the given conditions exhibited free monomer. Some standard formulations are presented in order to assess the properties of TMPME as monomer as well as the benefits of this building block in acrylic polyols.

Experimental
Table 2 shows the standard formulations used to assess the properties of TMPME as functional monomer in acrylic polyols compared to standard hydroxyl-functional monomers. All formulations have been chosen to have the OH number in the same range and the ratio of styrene/butyl acrylate by weight to be 2/1.Syntheses were carried out in a nitrogen atmosphere at 150 ºC simultaneously dropping the monomer blend and initiator (in xylene) over a 5-hour period. Only Formulation 4 used a xylene/n-butanol solvent blend in order to tackle the high viscosity during the synthesis and was lowered in non-volatile content at the level of 65%.
The experiments using TMPME as hydroxyl-functional monomer were carried out using the TMPME in a solution of xylene in which, at reflux, the radical initiator xylene solution and the styrene and butyl acrylate blend were loaded simultaneously drop-wise over a period of 5 hours (in similar conditions as for all other hydroxyl functional monomers).
The complete reaction of TMPME was confirmed by the absence of the double bond in the IR spectra and by the attempt to extract the free monomer with water from a diluted polymer sample. All water extracts had a zero non-volatile content showing that the TMPME had been completely reacted. The residual initiator was destroyed by maintaining the polymer at 150 ºC under nitrogen flow and verified over time using kalium iodine (KI) solution.



Although the acrylic backbone has higher molecular weight, the presence of the pendent fatty acids shields the higher Tg of the backbone and at the same time reduces the availability of H bonding between polymer chains.

Isocyanate Curing of Hydroxyl-Functional Copolymers
The hydroxyl-functional acrylic binders were cured at room temperature with polyisocyanate Desmodur 3790®. The curing performance is shown in Figure 8. All trials were carried out at a ratio of 1:1 hydroxyl to isocyanate.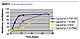
Formulation 4 has not been tested following the addition of n-butanol for high-viscosity reduction. The hardness is comparable for all copolymers, but the pot life is different. 2-HPMA has a long pot life that may be explained by the presence of secondary hydroxyl groups. The copolymer containing 2-HEA has a lower reactivity due to the fact that the hydroxyl group, although a primary group, is too close to the polymer backbone, thus presenting lower mobility. The copolymer containing hydroxyl groups from the 4-HBA has a shorter pot life, probably due to the higher mobility of the hydroxyl groups positioned at a longer distance from the backbone. The copolymers functionalized from TMPME may suffer from a combined effect from the vicinity and steric hindrance; as expected, one of the two hydroxyl groups in position 1,3 should react first, and then the second group at a slower rate, being already trapped in the newly generated network.

Curing with Melamine Resins
Curing of the hydroxyl-functional poly(styrene-acrylic) resins was performed at 140 ºC for 35 minutes. The melamine resin used for cure is a blend of melamine and toluene sulfonamide at a molar ratio of approximately 10:1 by mol. The application was done at a constant non-volatile content of 60% and a ratio of styrene-acrylic resin/amino resin 68/32 calculated on solids (Table 3).

Alkyd Resins with Copolymer Backbone
Table 4 lists the alkyds synthesized using the poly(styrene-acrylic) hydroxyl-functional backbones. As expected, the viscosity of the copolymer backbone esterified with fatty acids is lower than the viscosity of the starting (intermediate) copolymer, confirming the assumption that 1) the reduced hydroxyl functionality and 2) the shielding offered by the fatty acids acting as built-in solvent, both have strong effects in viscosity reduction. The viscosity of the alkyd resulting from a styrene-acrylic backbone modified with TMPME is lower than the alkyd from the backbone corresponding to the other hydroxyl functional monomer 2-HPMA. This may be explained by the presence of the ethyl group shielding the ester groups on the polymer backbone and hindering hydrogen bonding. The ethyl group from the TMPME has the effect of a ‘built in’ solvent, acting in viscosity reduction with a larger effect compared to the methyl group in the 2-HPMA, and also exhibiting a plasticizing effect. This is also reflected in the hardness of the alkyd as the ethyl group is reducing the physical drying lowering the Tg of the backbone.Conclusions
The present work recommends the use of TMPME as a hydroxyl-functional monomer for vinyl co-polymer backbones. The differences in reactivity for hydroxyl-functional co-polymers may be related to the mobility of the hydroxyl group, which is the distance between the functional group and the co-polymer backbone. The drying performance of hydroxyl-functional copolymers with amino resins and isocyanates is perfectly comparable, thus recommending the use of TMPME as a good replacement for sophisticated monomers. The use of TMPME always yields lower viscosity co-polymers when compared to the other existing options. Also the use of TMPME may lead to alkyd resins having a high non-volatile content and improved performance due to the high-molecular-weight backbone at a reasonable cost.Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Perstorp Specialty Chemicals (TMPME), Bayer AG, KOWA (4-HBA), Indochemical Citra Kimia (2-HEA, 2-HPMA) and Justus Kimia Raya (Styrene, Butyl acrylate), Arizona Chemicals (TOFA), for supplying the samples used in this experimental work. The authors are also thankful to Hendra Adidarma, Kris Adidarma, and Sugianto Effendi for making possible this investigation.
For further information, e-mail mircea.manea@telia.com.<
Bibliography
1. Holmberg, K. High solids alkyd resins, ISBN 0-8247-7778-6.2. Manea, M., et al, High solids alkyd strategy, Paint and Coatings Industry, July 2007.
3. DE3822995.
4. EP047061.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!








