Latest Developments in Water-Based 2K FEVE Coatings
for Applications Requiring Ultra-Weatherability

Fluoroethylene vinyl ether (FEVE) resins were developed in Japan in the late 1970s and entered the commercial market there in 1982. FEVE resins are amorphous A-B type copolymers with repeating units of fluoroethylene and substituted vinyl ether. Unlike pure fluoropolymers, FEVE resins are soluble in solvent due to the vinyl ether groups. Solvent solubility transforms FEVE resins from high-performance polymers into high-performance backbone resins for paints and coatings.
Fluoropolymers, like PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), were used in paints prior to the introduction of FEVE resins to the market. In fact, PVDF resins are still used widely today. In order to utilize these more traditional fluoro-polymers like PVDF in liquid coatings, blending with other resins such as acrylics is needed. Special solvents are required to solubilize the blends, and ultimately heat is used to help the system flow and form a thermoplastic coating film. In contrast, the FEVE polymer was designed to have inherent solubility in conventional, widely used solvents via vinyl ether monomers. The chemistry of the FEVE polymer also is fully amorphous, unlike the PVDF-acrylic systems that are semicrystalline. This amorphous morphology allows FEVE resins to form films without heat. The implication of this property is considerable. The introduction of FEVE fluoropolymers to the coatings industry brought extremely durable fluoropolymer coatings out of the factory and into the field.
The fluoroethylene groups are the strength of the FEVE resin. These groups are what make this class of polymers so resistant to UV degradation. The C-F bond is strong. The energy of this bond is ~486 kJ/mol2, while the energy of UV radiation at 300 nm is ~399 kJ/mol. The alternating pattern, shown in Figure 1, is critical for the extreme UV resistance properties. The chemically stable and UV-resistant fluoroethylene unit sterically and chemically protects the neighboring vinyl ether unit.3
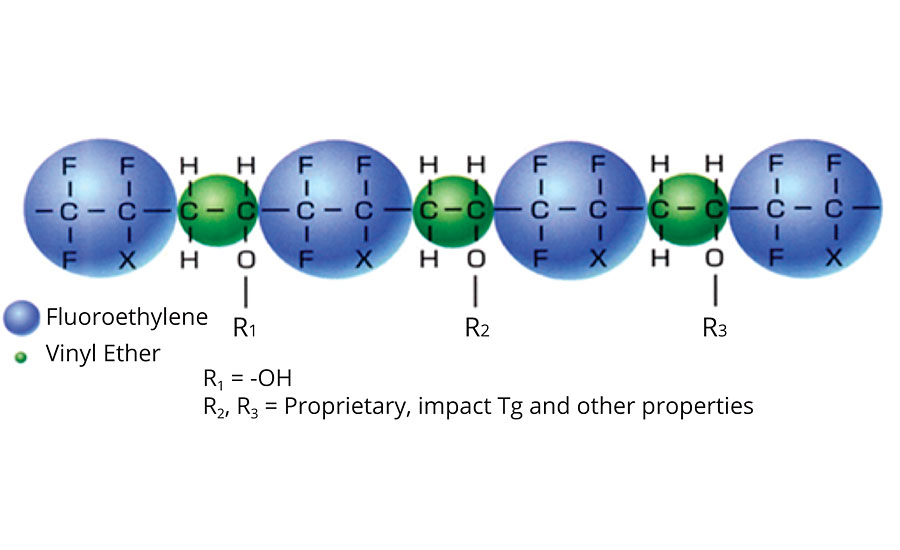
FIGURE 1 » Alternating structure of FEVE resins.
The vinyl ether groups make FEVE polymers useable as resins for paint. Without the vinyl ether groups, FEVE resins would not be soluble in solvent. This solubility is what allows FEVE resins to be used in a wide array of coating formulations that can be applied in factory or field settings.4 The vinyl ether groups also contribute to high gloss and allow for functional groups, like hydroxyl groups, to be incorporated into the structure. Table 1 shows typical properties of FEVE resins.
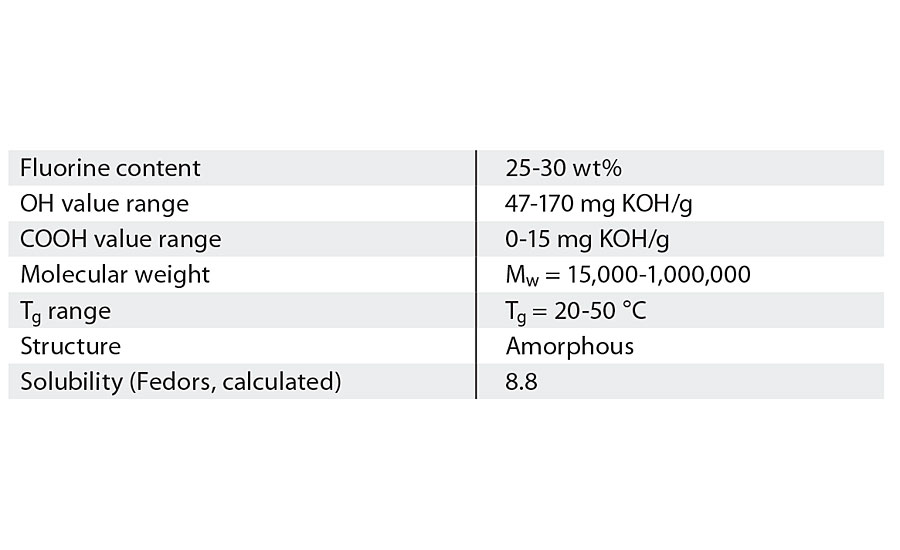
TABLE 1 » Typical properties of FEVE resins.3
Weathering Performance of Typical Solvent- and Water-Based FEVE Coatings
Weathering tests have shown that coatings based on FEVE resins have superior performance. This data has been discussed extensively in a previous study, and is shown in Figures 2-5.1,3
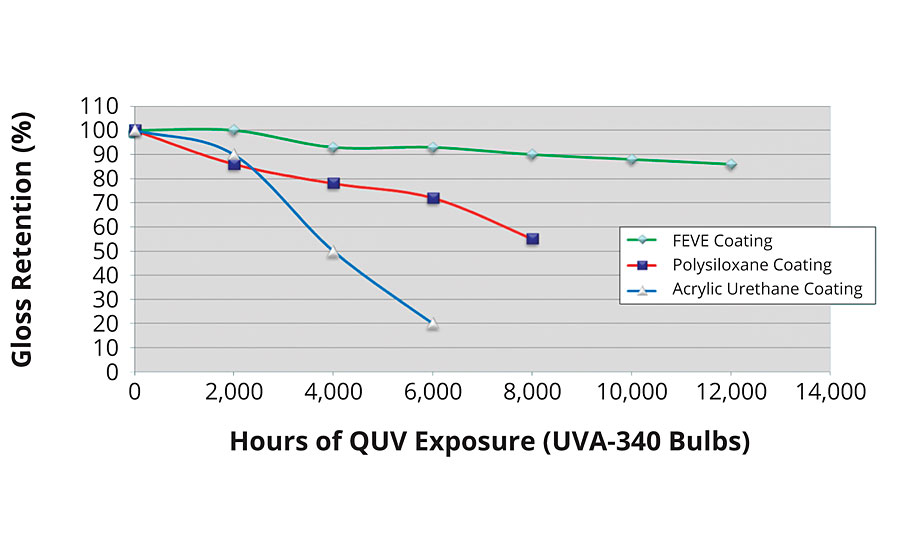
FIGURE 2 » QUV exposure of an FEVE-based coating.
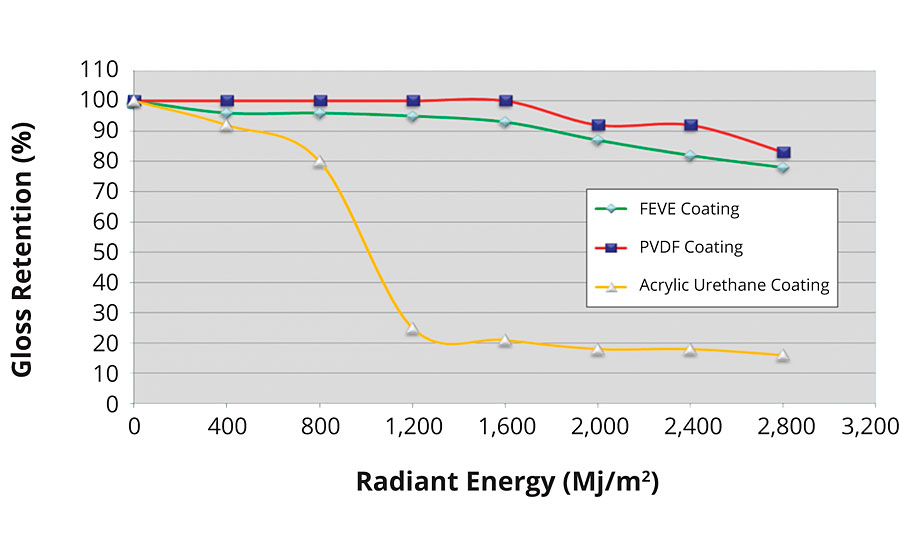
FIGURE 3 » EMMAQUA exposure of an FEVE-based coating.
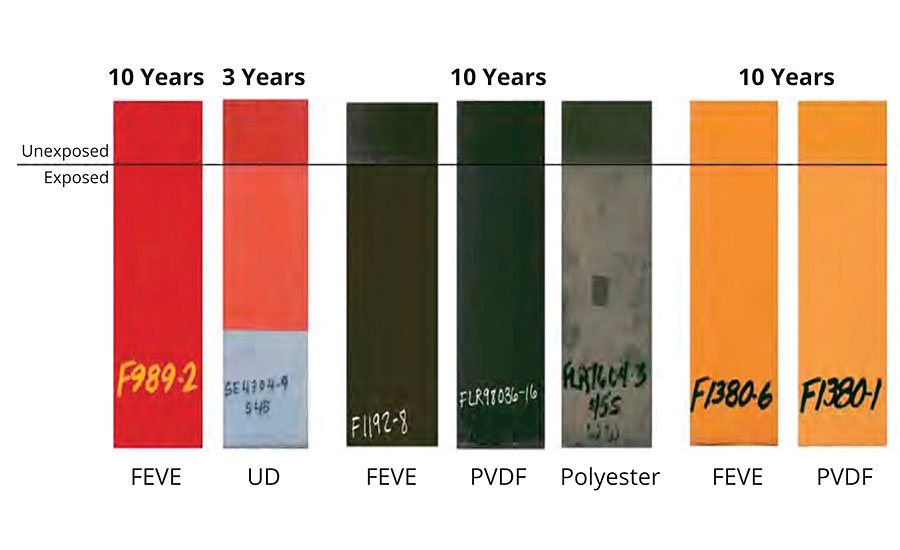
FIGURE 4 » A comparison of various coatings in South Florida exposure.
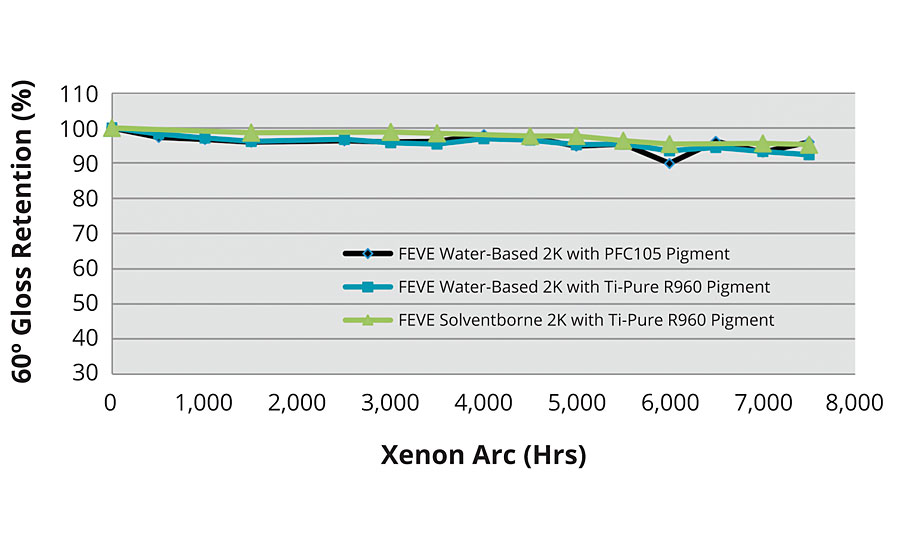
FIGURE 5 » Xenon arc exposure of water-based FEVE coatings.
Water-Based FEVE Resins for Highly Weatherable, Heavy-Duty Coatings
Weathering testing has shown that 2K water-based coatings based on FEVE resins perform comparably with solvent-based 2K FEVE coatings. As VOC regulations continue to tighten, the demand for heavy-duty water-based coatings will rise. The results of South Florida testing illustrate the high level of performance that can be achieved with FEVE 2K coatings (Figures 6-7).
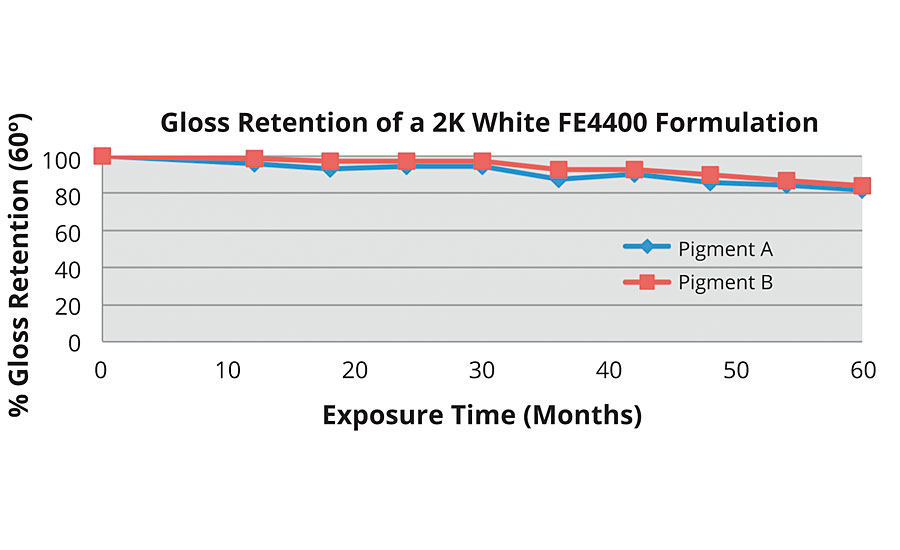
FIGURE 6 » South Florida exposure of a 2K coating based on an FEVE emulsion.
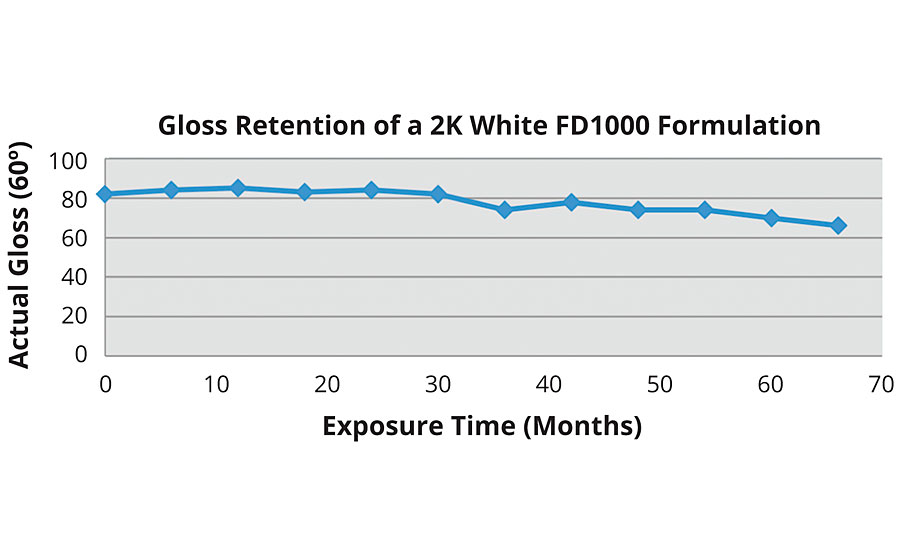
FIGURE 7 » South Florida exposure of a 2K coating based on an FEVE dispersion.
Formulating 2K water-based coatings is a challenge because of the competing reactions of polyol with NCO and water with NCO.
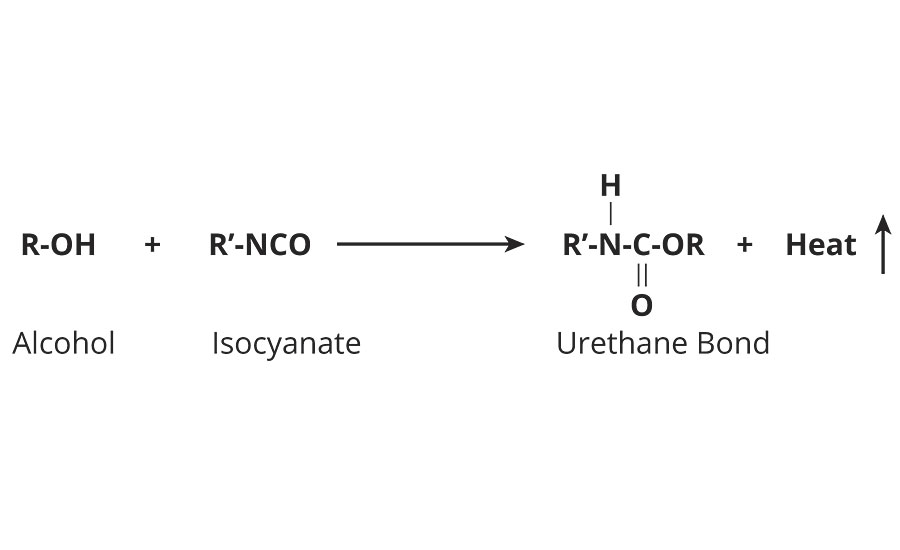
Equation 1 »
The reaction between water and polyisocyanate can result in the formation of polyurea instead of polyurethane. The following equation illustrates the reaction mechanisms involved.
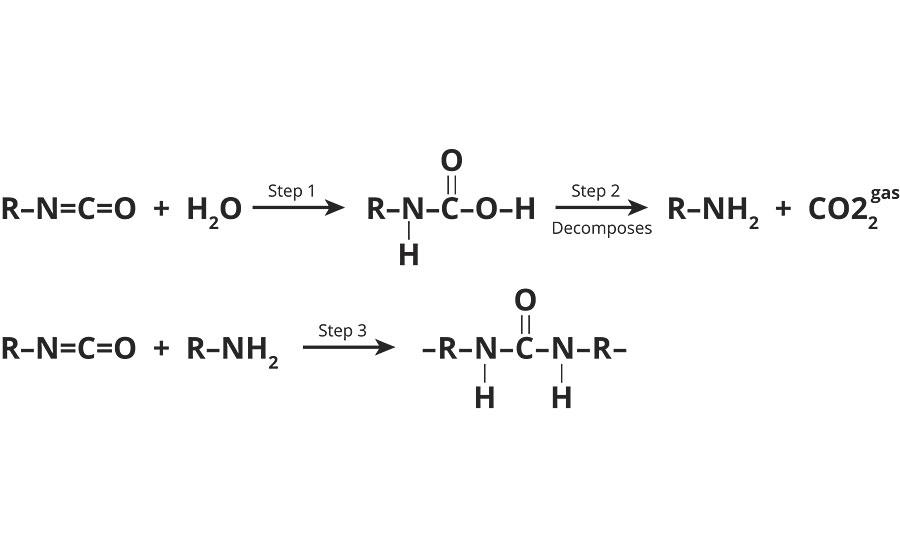
Equation 2 »
Another issue resulting from the reaction of water with polyisocyanate is the formation and evolution of carbon dioxide gas. If this occurs, it tends to happen throughout the pot life of the coating. This results in initial applications that appear nice, but subsequent applications may appear hazy. In severe cases, the gas bubbles can actually be seen with the naked eye.
Several approaches are available to overcome these challenges. One method is to use increased levels of polyisocyanate, often called over-indexing. The theory is that enough NCO will be available to react with water and the polyol. Another, less-common approach is to use catalysts specifically designed for water-based 2K systems.
Previous work1 showed the results of both of these approaches. The results yielded excellent weathering and corrosion resistance, but limited MEK double rubs. This indicated that the cure of these systems might not be optimal. A study (Figure 8a) was designed to better understand the factors affecting performance in MEK double rubs. The results suggest that many factors impact performance in this test.
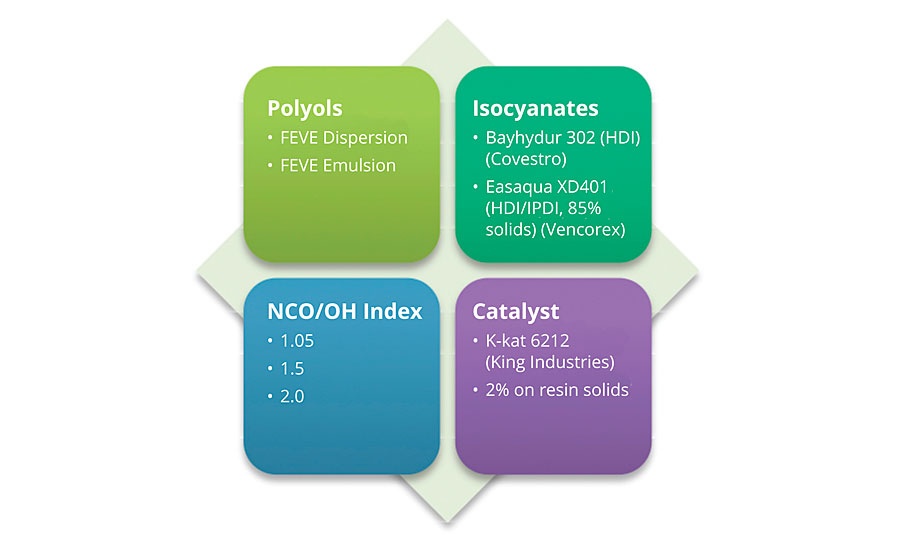
FIGURE 8a » Design matrix for MEK double rub study.
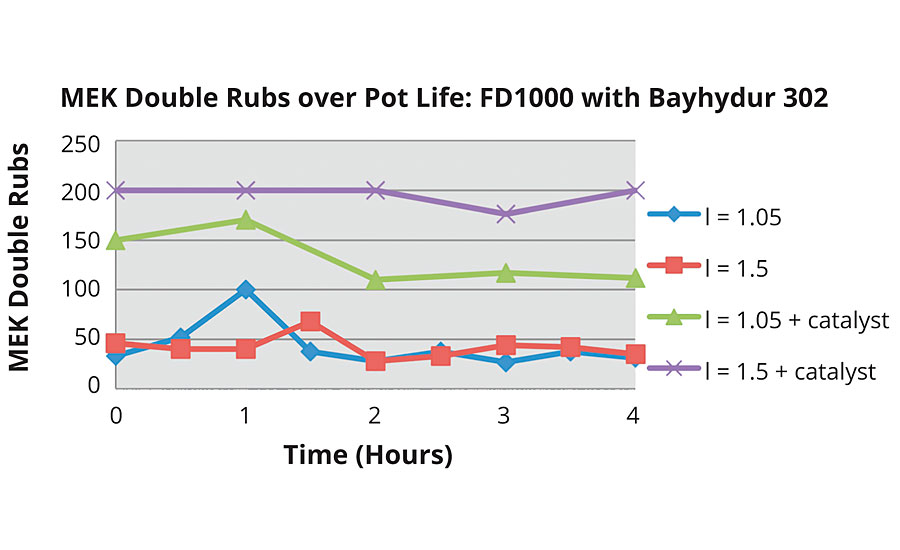
FIGURE 8b » MEK double rubs of an FEVE dispersion with an HDI NCO.
Formulations were made and MEK double rubs were tested over the course of the pot life of each system. Analysis of the impact of NCO:OH index and the presence of catalyst were performed first. Figure 8b shows clearly that the addition of catalyst significantly improves MEK double rubs. An increase in index makes a difference in combination with catalyst but not alone. This was seen in a study done previously1 with the FEVE dispersion, shown in Figure 9.
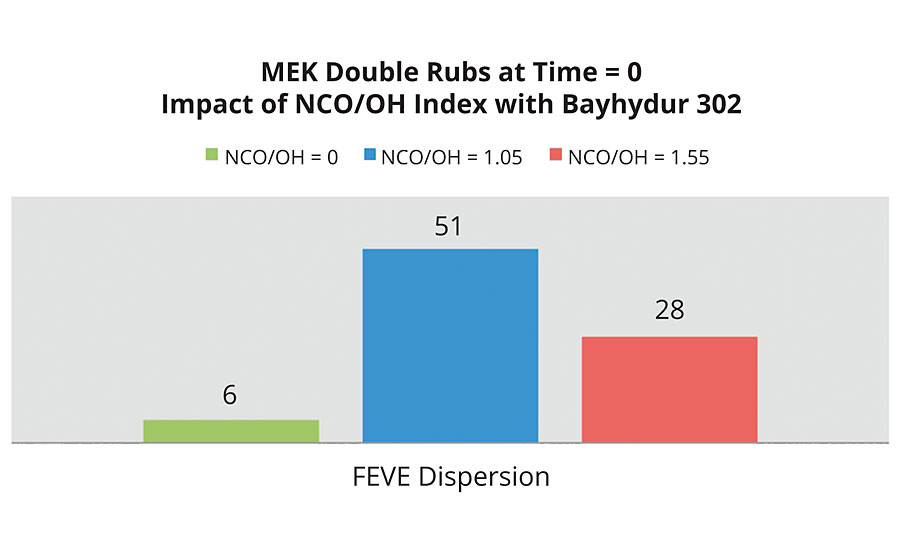
FIGURE 9 » MEK double rubs of an FEVE dispersion as a function of NCO:OH index.
When testing the FEVE dispersion with a different isocyanate, the impact of NCO:OH index seems more critical than the use of catalyst (Figure 10).
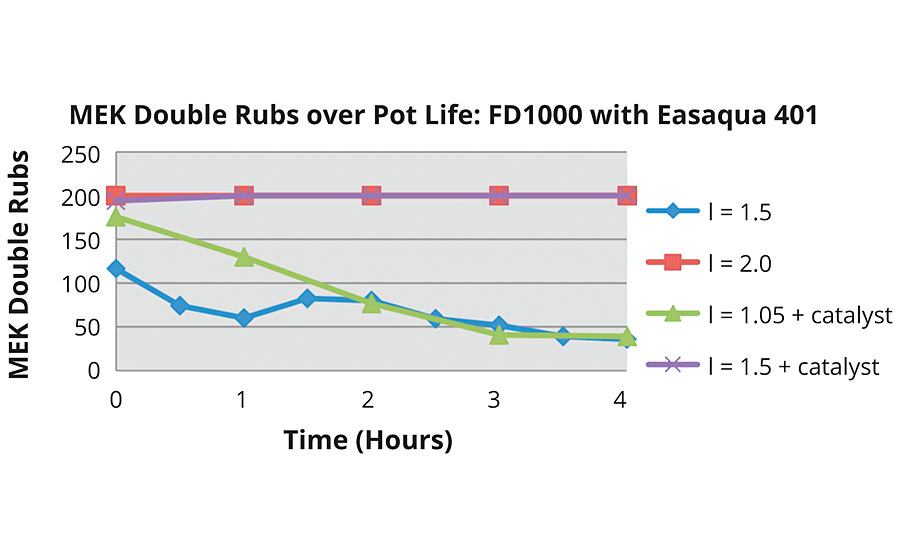
FIGURE 10 » MEK double rubs of an FEVE dispersion with an HDI/IPDI NCO.
Similar tests were done with the hydroxyl functional FEVE emulsion (Figure 11). The emulsion in combination with Easaqua™ XD401 had slightly better initial MEK double rubs but followed a similar trend as the FEVE dispersion with Easaqua XD401 over the course of the four-hour pot life study.
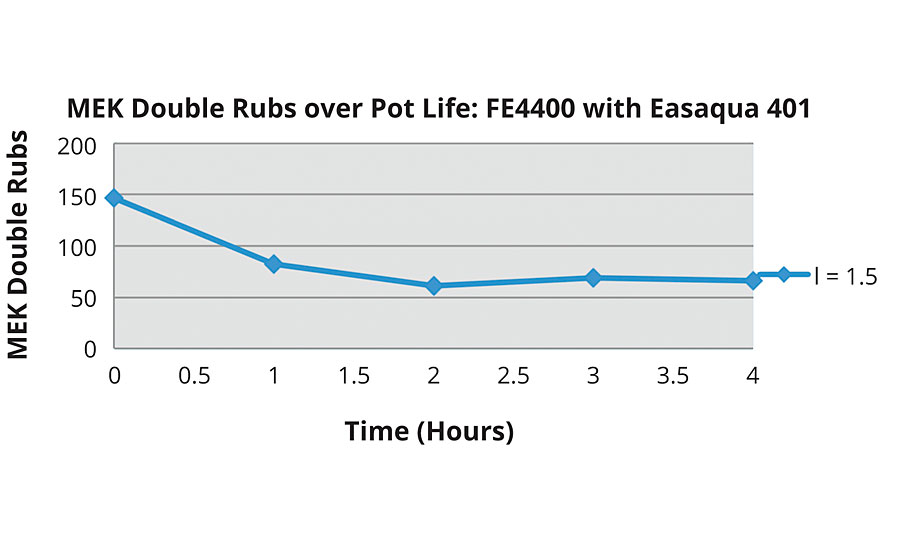
FIGURE 11 » MEK double rubs of an FEVE emulsion with an HDI/IPDI NCO.
The FEVE emulsion fared much better with the Bayhydur® 302 isocyanate, even surpassing the FEVE dispersion with Bayhydur 302 (Figure 12).
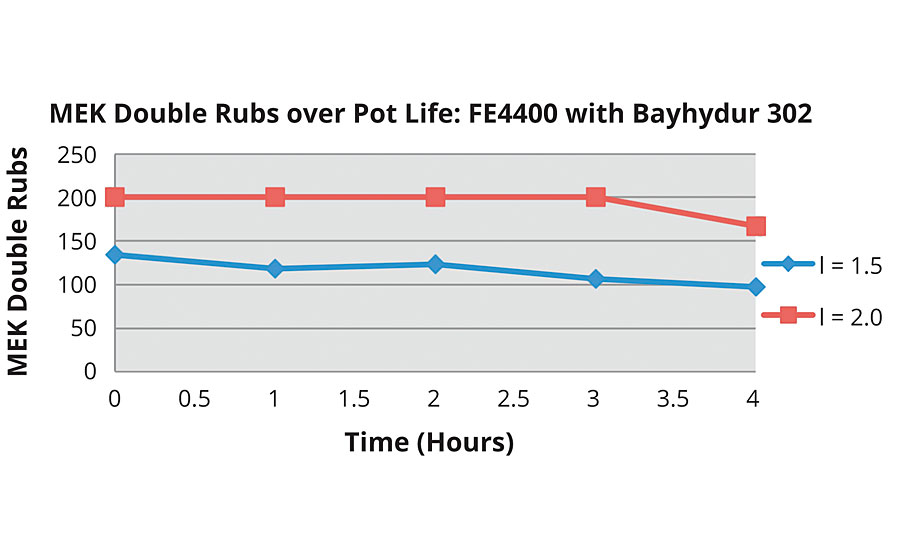
FIGURE 12 » MEK double rubs of an FEVE emulsion with an HDI NCO at two different indexes.
The previous analysis of the data looked at the impact of index and catalyst. In Figure 13, the impact of resin chemistry is reviewed at a constant index without catalyst.
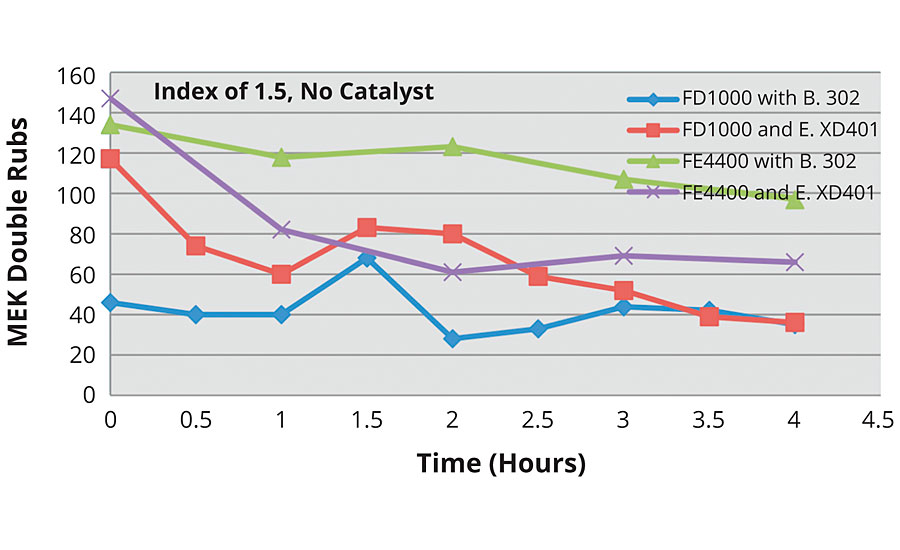
FIGURE 13 » MEK double rubs as a function of formulation chemistry at an index of 1.5.
The results indicate that all systems, save the FEVE dispersion with Bayhydur 302, have respectable initial MEK double rubs. However, over the pot life, the FEVE emulsion with Bayhydur 302 clearly outperforms the other systems.
The previous analysis showed the results of MEK double rubs over the course of the pot life. The results of the FEVE dispersion with Bayhydur 302 raise the question of whether an appreciable “sweat in” time is needed in the uncatalyzed systems because the highest MEK double rubs were not always seen initially, but after 30 min to an hour of pot life. This was not the case with the FEVE dispersion with Easaqua XD401 or with any of the emulsion systems.
It is important to note that the FEVE dispersion formulations did not require cosolvents, while the FE emulsion formulations did require cosolvents due to the higher Tg of the emulsion. It is also worth noting that the Easaqua XD401 is 85% solids in solvent, while the Bayhydur 302 is 100% solids. It is possible that the systems with cosolvent are very stable and well blended immediately after mixing, while the FEVE dispersions without cosolvent need time to blend well post-mixing. This needs to be studied further.
Common practice is to study degree of cure using MEK double rub testing right after mixing. The following graphs show the performance of all the systems at time zero. In Figure 12 the clear trend is that increasing index and the use of catalyst significantly improves initial MEK double rubs with the FEVE dispersion. In Figures 14 and 15 the trend of increasing index improving performance follows with the FEVE emulsion systems.
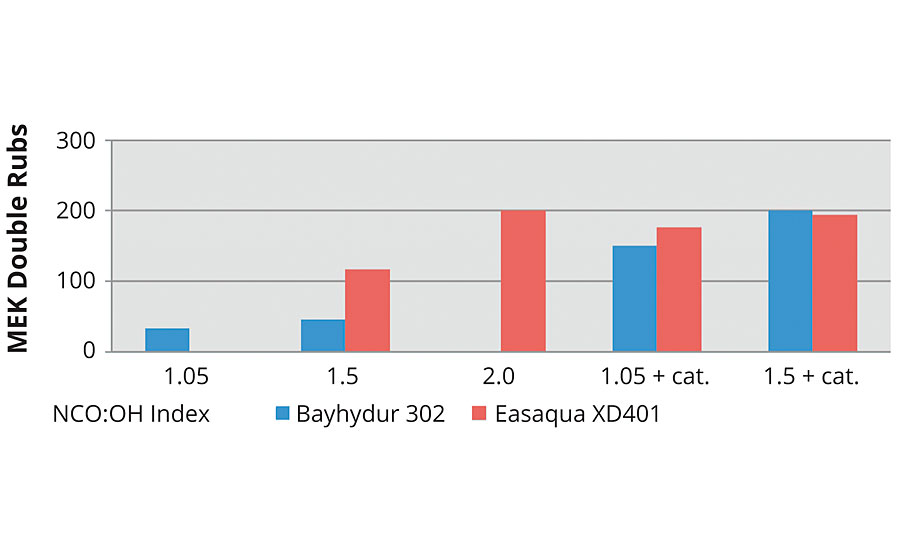
FIGURE 14 » MEK double rubs at time = 0 for an FEVE dispersion.
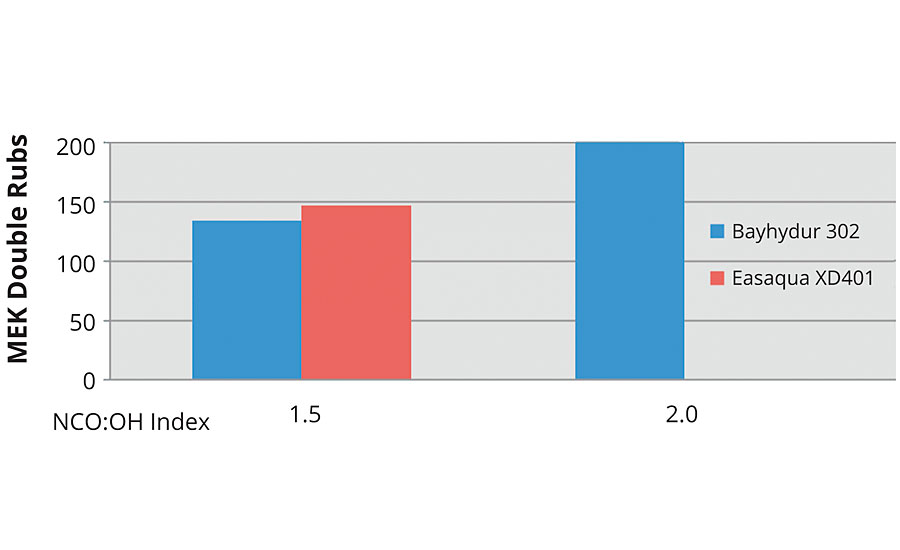
FIGURE 15 » MEK double rubs at time = 0 for an FEVE emulsion.
Table 2 shows the formulation used for the FEVE dispersion followed by the properties of that formulation.
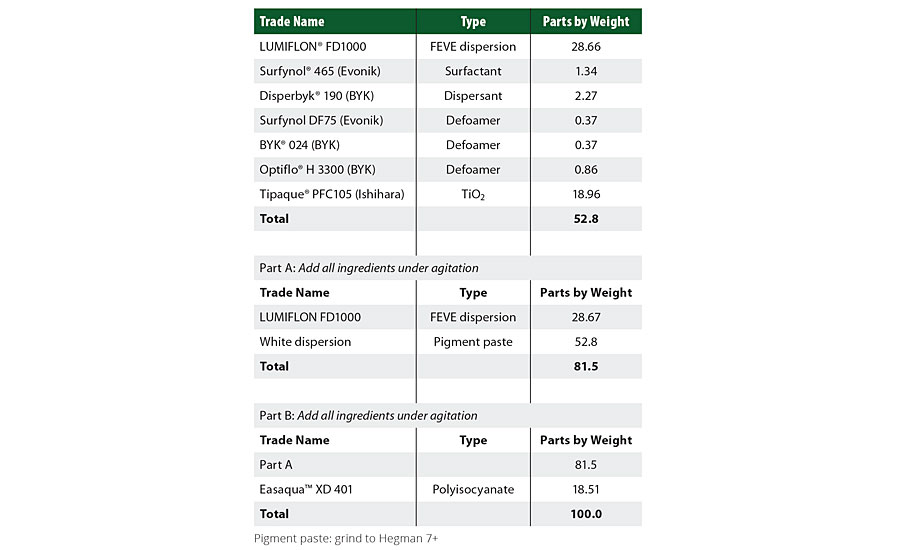
TABLE 2 » 2K white FEVE dispersion-based formulation at an index of 2.0.
Additional Testing in Progress
The aforementioned study shows that crosslinker, index, catalyst and possibly cosolvent level impact performance in MEK double rubs. All systems tested in this study have been put into QUV-A and Xenon Arc accelerated testing. Heavy-duty coatings used on metal substrates must also prevent corrosion; therefore, the formulations tested in this study are also being analyzed by EIS spectroscopy to determine barrier properties that are indicative of likely performance in corrosion testing. A physical property testing is also in progress.
Summary
FEVE fluoropolymer resins offer ultra-weatherability to solvent- and water-based coatings. As VOC regulations continue to increase, the need for heavy-duty water-based coatings also increases. However, formulating water-based 2K coatings presents many challenges. Though the results of accelerated and real-world, South Florida exposure testing were excellent, early analysis of degree of cure as measured by MEK double rubs was concerning.
Unlike the high levels that typical, high-performing solvent-based 2K coatings exhibit, preliminary testing of water-based 2K FEVE coatings were lower. Heavy-duty coatings for metal substrates need more than weatherability; they also need corrosion resistance. A better understanding of the factors affecting the cure in water-based 2K coatings was needed.
This study reviewed analysis of several formulations based on an FEVE emulsion and an FEVE dispersion. Results indicated that both the use of excess isocyanate (over-indexing) as well as specially designed catalysts for water-based 2K polyurethane coatings improve cure as measured by MEK double rubs. Formulations are currently being evaluated for weathering, corrosion resistance and physical properties.
References
1 Blankenship, K. Formulation and Performance Evaluation of Water-based 2K Polyurethane Coatings for Industrial Applications. The Waterborne Symposium: Proceedings of the Forty-third Annual International Waterborne, High-solids and Powder Coatings Symposium. 2016.
2 Ameduri, B.; Boutevin, B. Well-Architectured Fluoropolymers: Synthesis, Properties and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2004, p. 17.
3 Munekata, S.; Miyazaki, N.; Kaya, S.; Takayanagi, T. Characteristic Properties of LUMIFLON® as a Coating Material. Reports Res. Lab. Asahi Glass Co. Ltd. 1984, 34, 207.
4 Takayanagi, T.; Yamabe, M. Progress of Fluoropolymers on Coatings Applications Development of Mineral Spirit Soluble Polymer and Aqueous Dispersion. Progress in Organic Coatings. 2000, 40, 185-190.
This paper was presented at the 2018 Waterorne Symposium in New Orleans.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!







