Performance Characteristics of Coatings Containing Highly Fibrillated HDPE Fibers
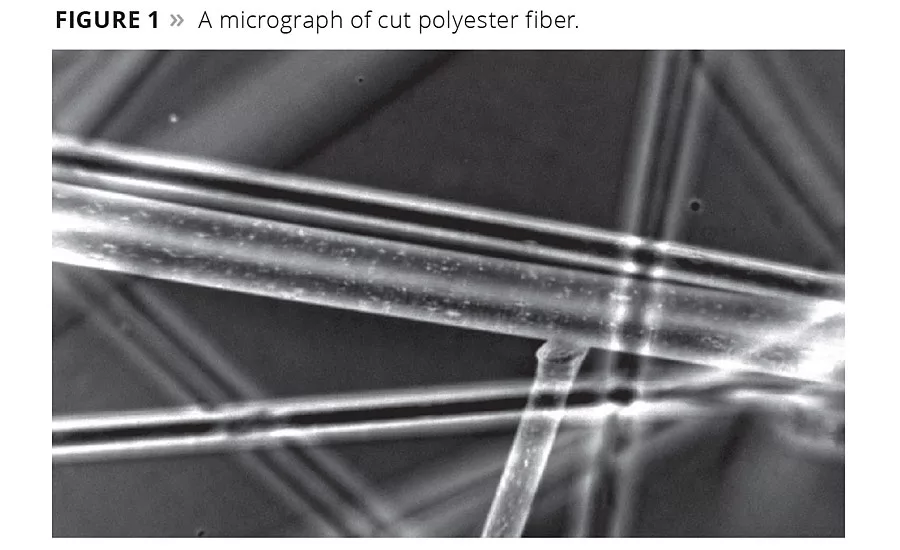
Figure 1
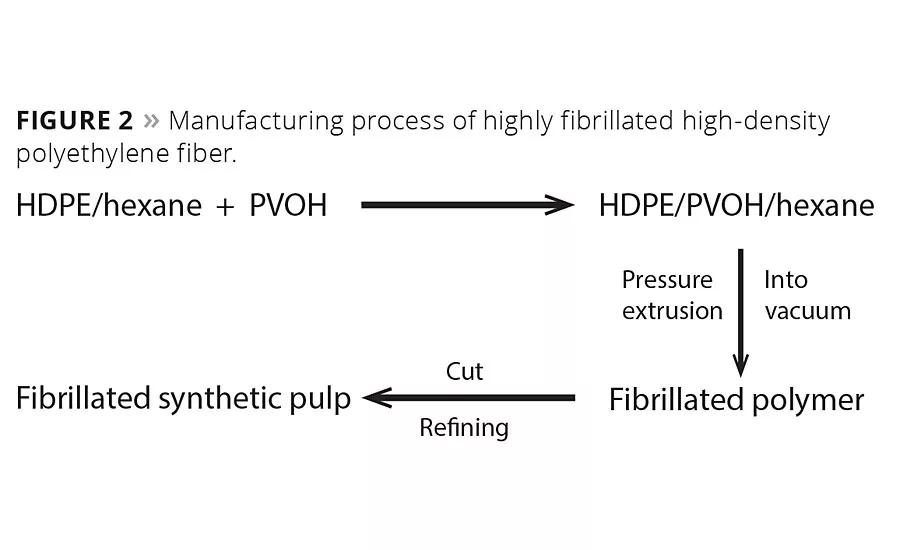
Figure 2
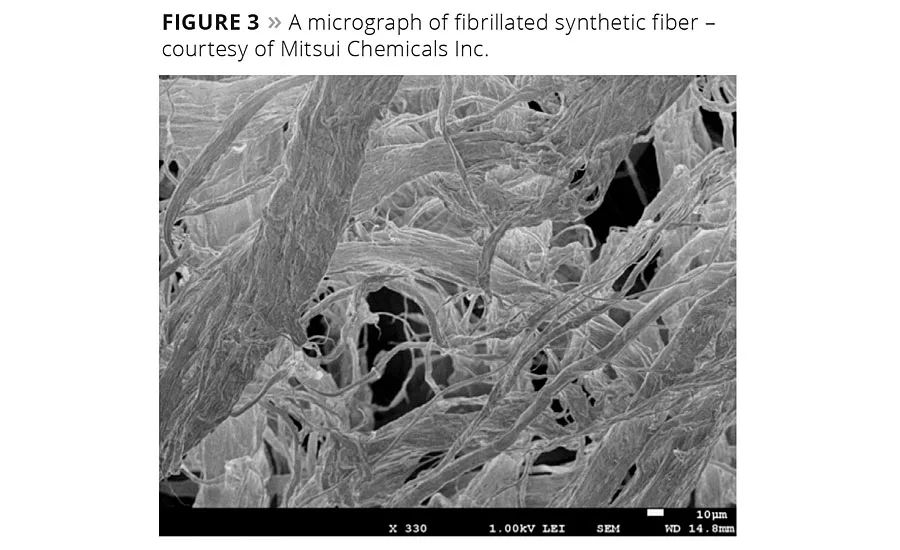
Figure 3

Figure 4
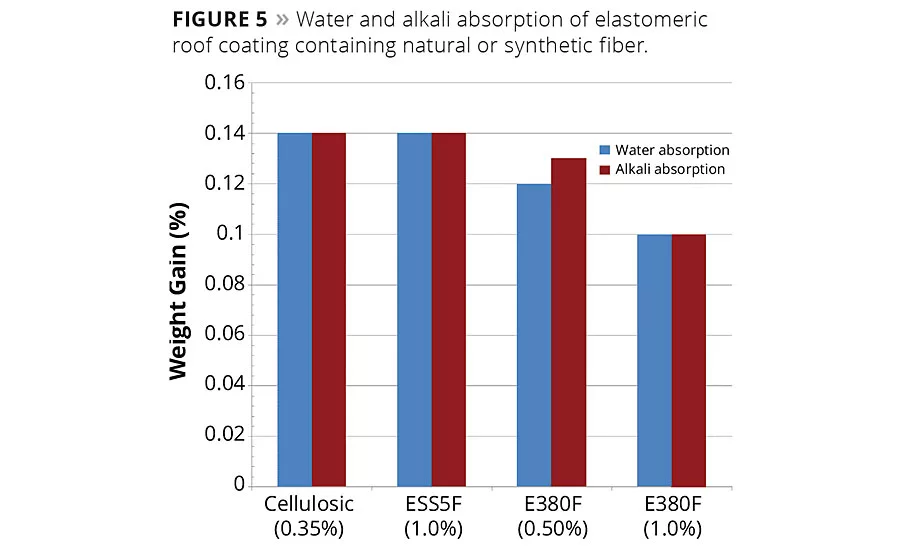
Figure 5

Figure 6

Figure 7
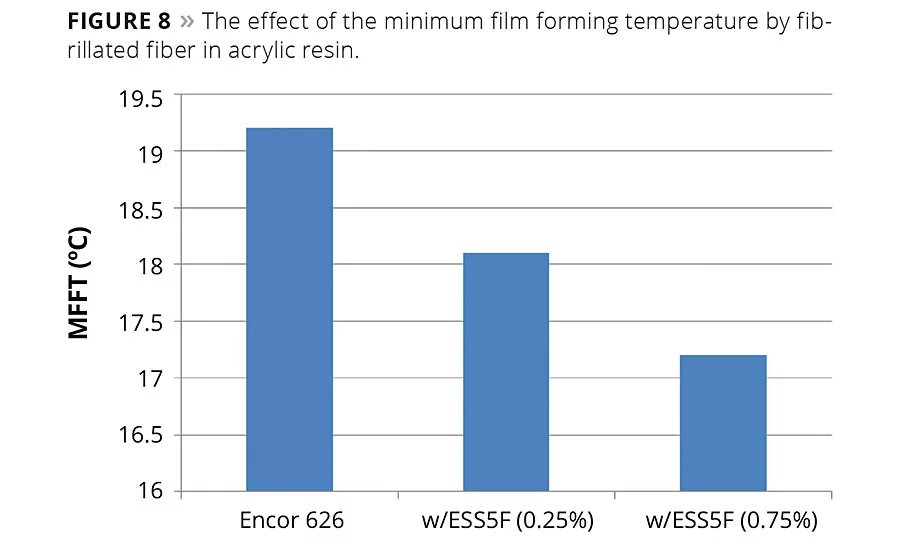
Figure 8
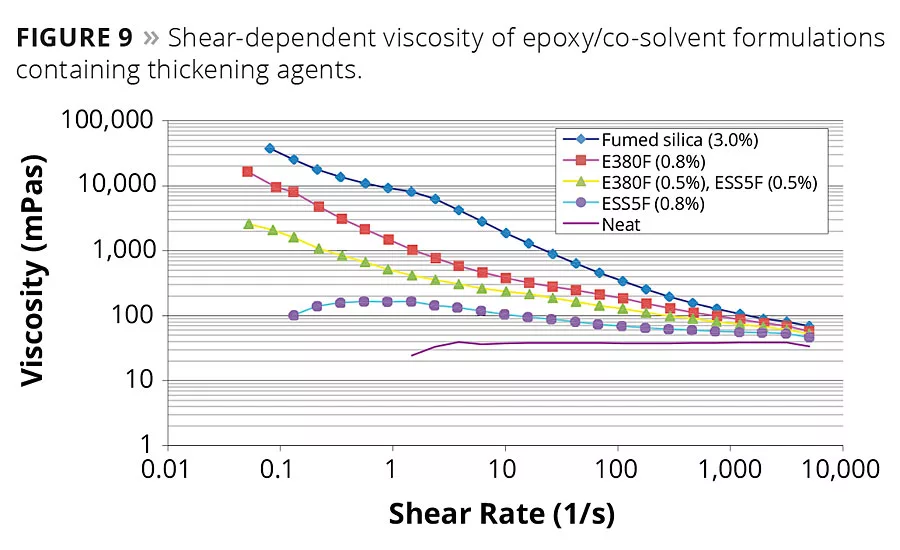
Figure 9
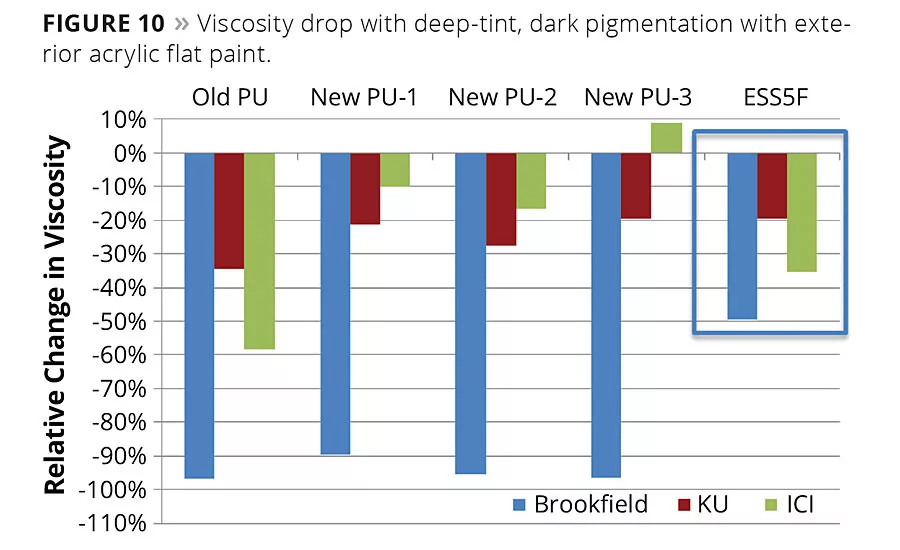
Figure 10
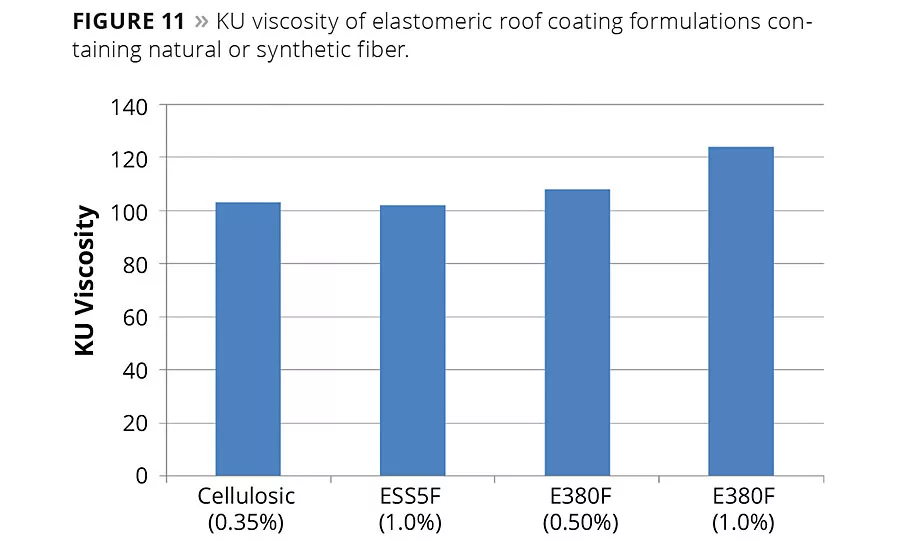
Figure 11
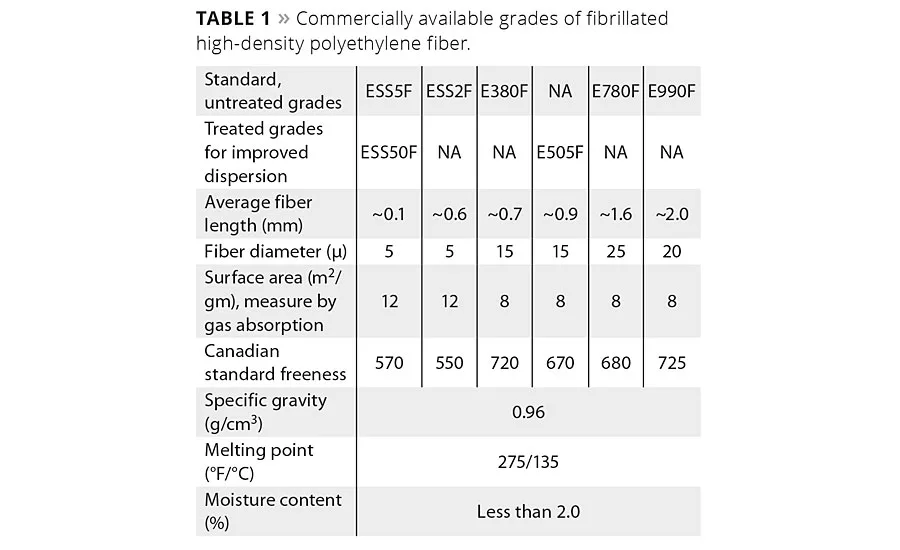
Table 1
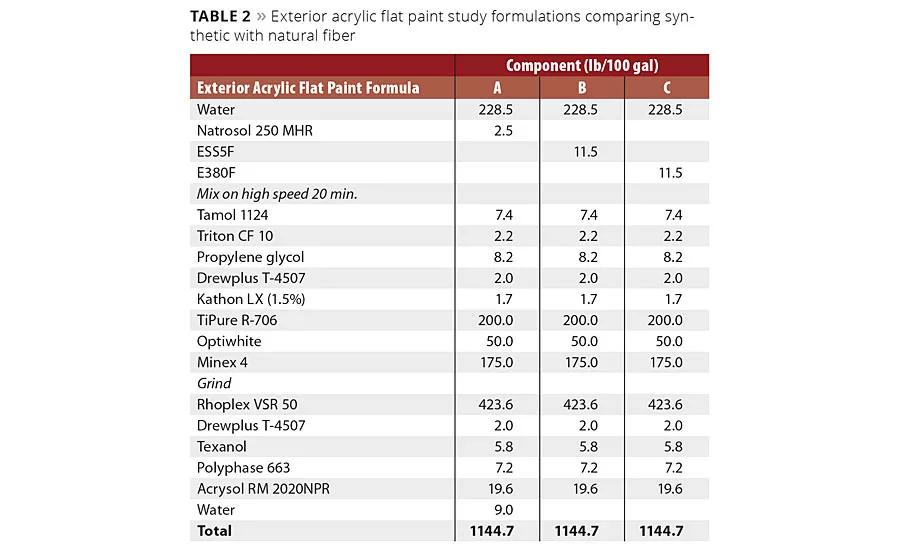
Table 2
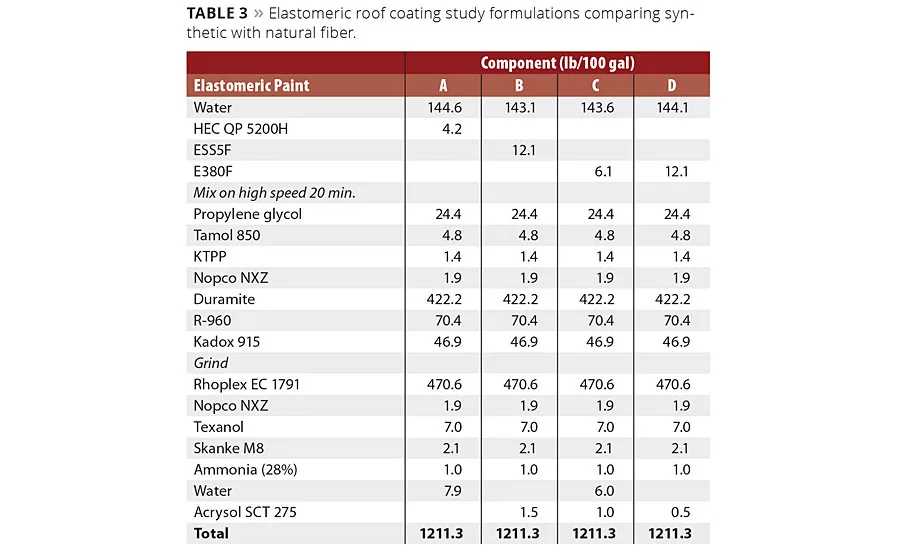
Table 3

Table 4
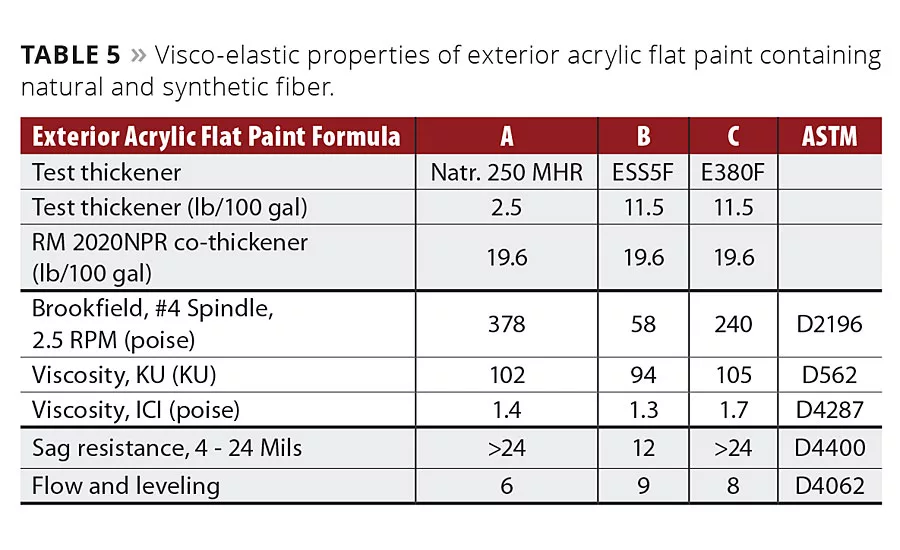
Table 5
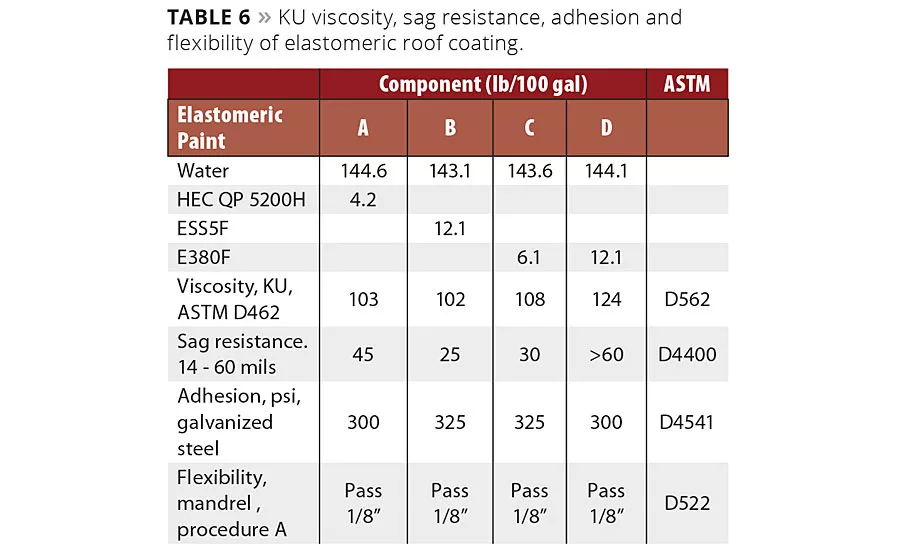
Table 6
Fibers have been an important part of human life for thousands of years. Most of what we wear is made of either natural fibers such as cotton or wool, or synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon. Synthetic fibers like polyester are made in a melt spinning process. This process gives the filaments the rod-like structure seen in Figure 1.
Preparation of Highly Fibrillated HDPE Fibers
In the 1970s, Crown Zellerbach sought to produce a synthetic wood pulp from high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Currently, this fiber is manufactured in this manner by Mitsui Chemical.1 This process is described in Figure 2.
High-density polyethylene is dissolved in hexane, and this solution is emulsified with a polyvinyl alcohol water solution. The emulsion is then extruded through a die into a heated vacuum with holes that determine the fiber’s diameter, which ranges from 5 µm to 25 µm. The highly volatile hexane flashes off vigorously, leading to a fiber that has a highly branched, or fibrillated, three-dimensional structure. The product is then cut to lengths ranging from 0.1 mm to 2.0 mm, depending on the grade, and then formed into a wet lap sheet. The main use of the fibers in this form is for heat-sealable filtration papers for coffee and tea.
These wet lap sheets are then processed further to separate the fibers into individual filaments and dry them to a moisture content of less than 2%. For coatings applications the grades of interest are the short- and medium-length fibers, with lengths between 100 µm to 900 µm, and diameters between 5 µm and 15 µm. Grades with enhanced dispersion in water-based systems are made with an additional treatment of polypropylene glycol. The physical properties of commercially available grades of fibrillated high-density polyethylene fiber are listed in Table 1.
Studies Performed
The benefits of fibrillated fibers in coatings include improved pigment suspension and prevention of hard settling, improved burnish resistance and stain resistance, improved water and alkali resistance, improved film ductility, reduced MFFT, predictable pseudoplastic rheology, reduced viscosity loss in deeply tinted systems, and advantages in Brookfield viscosity, sag reduction, and flow and leveling characteristics.
These benefits are described with the use of results obtained from studies performed on an exterior acrylic flat paint and an elastomeric roof coating.
Exterior Acrylic Flat Paint Formulation
A 100%-acrylic exterior paint was prepared at an independent laboratory,2 and tests were conducted comparing a cellulosic thickening agent with two different fibers; a short, fine fiber (ESS5F), as well as a medium-length and medium-diameter fiber (E380F). The formulations are depicted in Table 2. A broad range of paint tests were conducted including rheological tests, optical tests and film property tests. Observations and evaluations are presented in sections below.
Elastomeric Roof Coating Formulation
An elastomeric roof coating was prepared and tested by an independent laboratory2 in accordance with ASTM 6083. A cellulosic thickening agent was compared against two different fibers; a short, fine fiber (ESS5F), as well as medium-length and medium-diameter fiber (E380F). The formulations are depicted in Table 3. Observations and evaluations are presented in sections below.
Benefits of Highly Fibrillated Fibers
Particle Suspension
Highly fibrillated fibers have a complex structure with many interstitial voids. These can be seen in the micrograph of a single highly fibrillated polyethylene fiber, shown in Figure 3. This picture of a single fiber shows a main fibril, or branch, of approximately 25 µm and many smaller fibrils, some of which are less than 1 micron in size. This fiber has a specific gravity of 0.96 g/cc and will have a tendency to float in water. Typical pigments and fillers used in coatings are more dense and will have a tendency to sink in water. When these fibers are dispersed in water along with fine-particle-size pigments or fillers, the particles become entangled with the fiber. Once combined, the agglomeration of fiber and pigments or fillers form a unified density and stay suspended in the fluid. This is especially attractive to coatings formulators to prevent hard settling of pigments in coatings during storage.
This effect is demonstrated by a simple lab experiment in which sand, having a specific gravity of 2.6 g/cc and a mean particle size of 250 µm, is suspended in water by fiber. A mixture of 48% sand, 51% water and 1% fiber was prepared by hand shaking in a small jar. The resulting mixture is like an emulsion, which is shelf stable for many weeks. This effect is shown in the photographs in Figure 4.
Optical and Film Properties
Optical and film property test results of the acrylic exterior flat paint formulation described in Table 2 are depicted in Table 4. The optical properties of the film - opacity, tint, gloss and scrub resistance - were similar for all three paints. In addition, there is a small advantage in burnish resistance with the smaller fiber and a larger advantage in burnish resistance with the larger fiber. Also, stain resistance is favored slightly with fiber. Finally, accelerated weathering showed that fiber had no effect on performance. Along with these optical properties, longer fiber can be used at higher dosage to uniformly impart texture to the coating.
Water and Alkali Resistance
Water and alkali absorption of the acrylic elastomeric roof coating described in Table 3 are depicted in Figure 5. Of particular significance is that water and alkali absorption are dramatically reduced when the longer fiber is used. At 1% fiber loading, both water and alkali absorption are more than 30% less than with cellulosic thickener. This enhanced performance is thought to be due to the hydrophobic synthetic fiber that is dispersed throughout the coating, making the penetration of water energetically more difficult.
In another experiment, water resistance was observed with a 100% acrylic paint prepared with titanium dioxide and Barytes pigments. The first paint was made with no rheology modifier, the second was made with a cellulosic thickener, the third was made with 2% of the short synthetic fiber, and the last paint was made with cellulosic thickener at 0.1% and synthetic fiber at 1%. The paints were applied to glass panels, dried for 24 hrs and then immersed in water at 25 °C for 10 days. As depicted in Figure 6, the paints with fiber did not deteriorate and flake off, but the paints with no rheology additive and the one with only cellulosic thickener were significantly damaged.
Film Flexibility
In a separate experiment, these coatings were also subjected to a ductility test. In this comparison, the paint with only cellulosic thickener was compared to paint with a combination of cellulosic thickener and synthetic fiber. The paints were applied to a steel film, which was bent around successively smaller-diameter mandrels until the coating cracked and failed. Addition of the fiber allowed the paint to survive bending around a 6 mm rod, while the paint with just the cellulosic additive failed to survive bending around a 10 mm rod. These results are depicted in Figure 7 and demonstrate that the addition of synthetic fiber improves ductility.
Minimum Film Formation Temperature
Formulators have reported that formulations containing fibers exhibit improved coalescence properties in emulsion paints. In order to test this, minimum film formation temperature (MFFT) studies were conducted by the University of Southern Mississippi.3 A reduction in MFFT was expected if the fibers enable coalescence. As depicted in Figure 8, less than 1% of synthetic fiber clearly enhances coalescence and reduces the minimum film forming temperature of an acrylic resin.
Shear-Thinning Rheology
Formulators frequently use fumed silica to control the rheology of industrial paints that are not water based. For example, rheology modification of epoxy formulations by fumed silica is very common. As illustrated in Figure 9, an investigation of the rotational rheology of an epoxy resin diluted with a standard co-solvent illustrates the differing performance of pseudoplastic rheology modifiers. While 3% fumed silica exhibits a greater overall thickening than one-quarter to one-third of that amount of synthetic fiber, including a slight dilatant tendency between 1 s-1 and 4 s-1 added synthetic fibrillated fiber produces a deeper (faster declining) shear-thinning effect upon viscosity. For example, 0.8% of the larger fiber exhibits a viscosity drop of more than ten-fold in going from a shear rate of 0.05 s-1 (16,500 cP) to 0.9 s-1 (1,480 cP), as compared with an approximate four-fold drop with fumed silica over the same shear range. Of interest is the thickening trend exhibited as the diameter and length of the fiber increases from 5 µm x 100 µm (0.8% ESS5F) to 15 µm x 700 µm (0.8% E380F), respectively. Also of practical importance is the intermediate performance of a blend of the two fiber grades (), the ratio of which offers unlimited viscosity property latitude to a coatings formulator. Typical experience in the field indicates that a loading of one fourth the level of fumed silica will achieve comparable rheological performance.
Viscosity Drop Reduction in Deeply Tinted Paints
Controlling the viscosity of deeply tinted paints continues to be a problem for the industry. Dispersants and surfactants used in the rheology modifiers interact with those present in the tint base, and sharp drops in viscosity occur. Consequently, the shortest fiber was evaluated alongside several polyurethane (PU) thickeners to see if the fiber’s physical rheology functionality was more immune to this phenomenon. Paints were made and Brookfield, KU and ICI viscosities were measured for the untinted base paint. These parameters were then measured after tinting with 8 oz. per gallon of universal lamp black. Depicted in Figure 10, these results demonstrate that the fiber was much more effective in preventing the steep drop in Brookfield viscosity that typically accompanied PU-thickened paints. Further research is being conducted to determine the effects of a combination of fiber with the best-performing PU thickener.
Viscosity and Flow Properties
Brookfield, KU and ICI viscosities, sag resistance, and flow and leveling characteristics of the exterior acrylic flat paint formulations described in Table 2 are depicted in Table 5. The short, fine fiber (ESS5F) contributed less viscosity in all three regions when compared with the cellulosic-thickened paint. The longer, thicker fiber (E380F) gave much more viscosity in all three regions compared to the shorter fiber. This is the first important rule that was discovered. At the same addition rate, a longer fiber will give more viscosity than a shorter fiber. It is believed that this rheological performance is developed physically. When dispersed, the fibrils are spread open, and when the fluid is sheared they fold in, reducing viscosity. When the shear is removed the arms spread out again, almost instantaneously, and viscosity is recovered (very little hysteresis). Sag resistance is consistent with rheology. The shorter fiber gives less sag resistance than the larger fiber, which is similar to the cellulosic thickener. These film property tests reveal a very interesting and unique comparison. While increasing sag resistance, the fiber also exhibits an improvement in flow and leveling properties. Fibril capillary action with the synthetic fiber at rest is believed to be responsible for improved paint flow and leveling while simultaneously reducing sag.
Another comparison was made in a separate study with the elastomeric roof coating formula depicted in Table 3. Two addition levels of the larger fiber (E380F) were tested against the higher dosage of the short fiber (ESS5F) and the control formula thickened by a cellulosic additive. In terms of rheology, the loading of the longer fiber gave more rheology than that of the shorter fiber. This is because the longer fiber has larger fibrils, which extend into the fluid further and provide more resistance to flow. The related KU viscosity data (ASTM D462) is depicted in Table 6 and Figure 11.
Also illustrated in Table 6, sag resistance (ASTM D4400) followed this rheological trend with the following order of sag resistance: longer fiber (1%) >> longer fiber (0.5%) > cellulosic (0.35%) > shorter fiber (1.0%). Adhesion to galvanized steel (ASTM 4541) and flexibility (ASTM 522) are acceptable with all of the coatings.
Conclusions
Highly fibrillated HDPE fiber is a remarkable additive for coatings. Laboratory testing has confirmed a number of interesting simultaneous benefits with which formulators can use to make improved coatings. These include:
- Improved pigment suspension and prevention of hard settling;
- Improved burnish resistance, stain resistance and weatherability;
- Elevated resistance to water and alkali;
- Higher film ductility;
- Reduction in MFFT;
- Predictable pseudoplastic rheology;
- A reduction in viscosity loss with dark pigments;
- Advantages in Brookfield viscosity, sag reduction, and flow and leveling characteristics.
References
1 Mitsui Chemicals, Inc., Shiodome City Center, 5-2, Higashi-Shimbashi 1-chome, Minato-ku, Tokyo 05-7117, Japan.
2 Marschall Laboratories Inc, 2060 Palmetto St, Clearwater, FL 33765.
3 University of Southern Mississippi, Thames Polymer Science Research Center, 118 College Drive, Hattiesburg, MS 39406-0001.
For more information, contact MiniFIBERS, Inc., 2923 Boones Creek Rd., Johnson City, TN 37615, www.minifibers.com.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!





