New Anti-Fingerprint Coatings
Keeping surfaces free of contamination from fingerprints and dirt, as well as making them easier to clean, is an active field of research and technology development.


To solve such problems relating to oil and water repellency, various stain-proofing agents have been previously proposed. One proposal was a stain-resistant anti-reflective coating obtained by surface treating a substrate with a perfluoroalkyl-group-containing compound. Another approach was a stain-resistant, low-reflection plastic that has a polyfluoroalkyl group containing mono and disilane compounds and halogen, alkyl, or alkoxysilane compounds as a surface-modification coating. A third option that has been proposed is forming a copolymer of perfluoroalkyl (meth)acrylate and alkoxy silane group containing monomer on an optical thin film mainly consisting of silicon dioxide. However, these coatings have insufficient stain resistance properties, especially on the most important stains such as fingerprints, skin oil, sweat and cosmetics.
Obtaining the desired performance of high water and oil contact angles and low sliding angles required chemical modification of a linear perfluoropolyether. Four alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether adducts were synthesized, as shown in Figure 1.
 After synthesis, a series of performance tests
was done to assess anti-staining performance. These silyl-modified perfluoropolyethers
[I] to [IV] were applied on glass test pieces. The anti-staining coatings were
applied both by CVD (chemical vapor deposition) and dip coating in a dilute
solution, as described in Figure 2.
After synthesis, a series of performance tests
was done to assess anti-staining performance. These silyl-modified perfluoropolyethers
[I] to [IV] were applied on glass test pieces. The anti-staining coatings were
applied both by CVD (chemical vapor deposition) and dip coating in a dilute
solution, as described in Figure 2.
 The impact of the alkoxysilyl structure of the modified
perfluoropolyether was evaluated while keeping the polyether chain length
constant (n = 20) using the dip coating application method. The surface
properties of the treated glass substrates were compared using static contact
angle and sliding angles of water and n-hexadecane (Table 1).
The impact of the alkoxysilyl structure of the modified
perfluoropolyether was evaluated while keeping the polyether chain length
constant (n = 20) using the dip coating application method. The surface
properties of the treated glass substrates were compared using static contact
angle and sliding angles of water and n-hexadecane (Table 1).
As can be seen in Table 1, high water and oil (n-hexadecane) contact angles were observed in all cases. The simpler alkoxysilyl group in [I] and [III] gave slightly higher static contact angles and slightly lower sliding angles for both water and n-hexadecane when compared with [II] and [IV]. The organic linking group between the Si and the perfluoropolyether backbone also had a slight impact on the results, with the amide-containing group [III/IV] giving lower water contact angles and high n-hexadecane contact angles. The results suggest that highly organized molecular arrangement of the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyethers can be achieved on this surface. In all cases the degree of surface hysteresis is small, as shown by the very low sliding angles.
 The effect of perfluoropolyether molecular
weight was evaluated by adjusting the degree of polymerization of the polyether
backbone (n) of structure [I]. Water and n-hexadecane contact and sliding
angles are summarized in Table 2 using the dip coating application
method.
The effect of perfluoropolyether molecular
weight was evaluated by adjusting the degree of polymerization of the polyether
backbone (n) of structure [I]. Water and n-hexadecane contact and sliding
angles are summarized in Table 2 using the dip coating application
method.
No clear trend was seen for the water and n-hexadecane contact angles although the data did suggest that as the perfluoropolyether molecular weight increased, the sliding angle for water also increased. For the n-hexadecane sliding angle there was no observable relationship with polymer molecular weight.
 Interestingly, the application method was found to have the most
significant impact on the contact angle. While the contact angle data was
similar for the two application methods, the CVD application method gave
significantly higher sliding angle for water regardless of the molecular
weight, as shown in Table 3. This behavior would seem to suggest that
components present in the products that can be deposited on the glass surface
by dip coating are not deposited by the CVD method due to their higher boiling
point. However, the n-hexadecane sliding angle is not affected by application
method.
Interestingly, the application method was found to have the most
significant impact on the contact angle. While the contact angle data was
similar for the two application methods, the CVD application method gave
significantly higher sliding angle for water regardless of the molecular
weight, as shown in Table 3. This behavior would seem to suggest that
components present in the products that can be deposited on the glass surface
by dip coating are not deposited by the CVD method due to their higher boiling
point. However, the n-hexadecane sliding angle is not affected by application
method.
 The product recently developed as a result of the alkoxysilyl
perfluoropolyether synthesis, Dow Corning® 2604 Coating, was
compared on a glass substrate to a common anti-staining material (C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3)
and a control sample with no surface treatment. Measurements of water and
n-hexadecane contact angle and sliding angle gave the results in Table
4.
The product recently developed as a result of the alkoxysilyl
perfluoropolyether synthesis, Dow Corning® 2604 Coating, was
compared on a glass substrate to a common anti-staining material (C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3)
and a control sample with no surface treatment. Measurements of water and
n-hexadecane contact angle and sliding angle gave the results in Table
4.
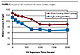 Water and n-hexadecane contact and sliding angles are important after
aging to ensure the surface is resistant to the elements of a given application
and will provide anti-stain performance over time. Using UV exposure and
rubbing durability of the treated surface are methods commonly used to predict
the effective life of the surface modification. The impact of UV exposure on
water contact angle was determined using a Sunshine Weather-O-Meter and
compared to the commercially known surface treatment known as C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3
(Figure 3). There was a significant improvement of UV irradiation resistance of
the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether as measured by water contact angle over the
test period.
Water and n-hexadecane contact and sliding angles are important after
aging to ensure the surface is resistant to the elements of a given application
and will provide anti-stain performance over time. Using UV exposure and
rubbing durability of the treated surface are methods commonly used to predict
the effective life of the surface modification. The impact of UV exposure on
water contact angle was determined using a Sunshine Weather-O-Meter and
compared to the commercially known surface treatment known as C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3
(Figure 3). There was a significant improvement of UV irradiation resistance of
the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether as measured by water contact angle over the
test period.
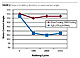 The effect of rubbing durability is also a key parameter when
considering the use of the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether coating on surfaces
that are subjected to physical wear. Applications such as ophthalmic lenses,
camera lenses, portable electronic devices and auto interiors require
resistance to rubbing to ensure long-term hydrophobic and oleophobic
properties. Durability testing is typically carried out using a device that
applies a constant pressure on a uniform surface area that cycles from side to
side across the surface. The glass test pieces were subjected to a 500-gram
force applied by a cotton cloth fixed to an aluminum block. Water contact angle
is measured after various intervals to obtain the relationship with rubbing
cycles. A comparative method is typically needed to assess durability as there
are no absolute pass/fail values (Figure 4).
The effect of rubbing durability is also a key parameter when
considering the use of the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether coating on surfaces
that are subjected to physical wear. Applications such as ophthalmic lenses,
camera lenses, portable electronic devices and auto interiors require
resistance to rubbing to ensure long-term hydrophobic and oleophobic
properties. Durability testing is typically carried out using a device that
applies a constant pressure on a uniform surface area that cycles from side to
side across the surface. The glass test pieces were subjected to a 500-gram
force applied by a cotton cloth fixed to an aluminum block. Water contact angle
is measured after various intervals to obtain the relationship with rubbing
cycles. A comparative method is typically needed to assess durability as there
are no absolute pass/fail values (Figure 4).
As can be seen from Figure 4 there is a significant difference in the resistance to rubbing as measured by water contact angle. After 5000 cycles the commercial C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3 material has an 8° reduction in water contact angle, while the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether shows only a 1° change. The decrease in contact angle of the C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3 material takes effect before 1000 rubbing cycles, and is then constant at 103° for the balance of the test period.
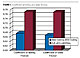 Ease of cleaning can also be improved by the new
alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether technology. A comparison of sliding and static
coefficients of friction provides a comparative insight into the easy-to-clean
property (Figure 5). The lower sliding and static coefficients of friction
predicate that the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether will have both better
stay-clean and easy-to-clean characteristics.
Ease of cleaning can also be improved by the new
alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether technology. A comparison of sliding and static
coefficients of friction provides a comparative insight into the easy-to-clean
property (Figure 5). The lower sliding and static coefficients of friction
predicate that the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether will have both better
stay-clean and easy-to-clean characteristics.
This paper was presented at the 11th Annual Coatings for Plastics Symposium, Chicago, IL, April, 2008.
For information about Dow Corning’s fluorosilicone coatings, contact Steve Block at steve.block@dowcorning.com or visit www.dowcorning.com/coatings.

Introduction
Achieving oil and water repellency on surfaces is easily obtained with the use of fluoroalkyl-modified silanes. While perfluoroalkyl-modified silanes exhibit high static and advancing water and oil contact angles, their low receding contact angles mean the oil and water will not readily slide over the treated surface. The resulting effect of these characteristics yields a surface that is both easy to clean and stays clean longer. Ultimately, modified perfluoropolyether silanes give high static and advancing water and oil contact angles as well as high receding contact angles resulting in a very low sliding angle. The influence of structure modification of the silane and the perfluoropolyether component is examined, and their impact on performance by application method is discussed in this paper.
Results and Discussion
The goal of these improvements is a surface modified for use in forming a low-surface-tension layer or a dirt-preventive layer on the surface of various substrates and a method for applying the coating material. A wide range of uses will benefit from these surface improvements including applications such as optical members (e.g., anti-reflective films, optical filters, ophthalmic lenses, mirrors), electronic display screens (e.g., liquid crystal displays, CRT displays, plasma displays, projection TVs), consumer appliances, treated glass, and earthenware. Surfaces that are routinely subjected to touch are commonly stained with fingerprints, skin oil, sweat and cosmetics when used. Once the surface is contaminated, the stains are not easily removed, or cleaning materials are needed. Dirt and fingerprints on surfaces that have an anti-reflective coating are very sensitive to surface contamination and cause not just an unpleasant aesthetic appearance but can also result in safety issues. Obtaining a surface that is resistant to fouling and has long-term surface performance durability becomes another hurdle in challenging applications like automobile windows, handheld electronic devices, and kitchen appliances, which all have frequent skin contact.To solve such problems relating to oil and water repellency, various stain-proofing agents have been previously proposed. One proposal was a stain-resistant anti-reflective coating obtained by surface treating a substrate with a perfluoroalkyl-group-containing compound. Another approach was a stain-resistant, low-reflection plastic that has a polyfluoroalkyl group containing mono and disilane compounds and halogen, alkyl, or alkoxysilane compounds as a surface-modification coating. A third option that has been proposed is forming a copolymer of perfluoroalkyl (meth)acrylate and alkoxy silane group containing monomer on an optical thin film mainly consisting of silicon dioxide. However, these coatings have insufficient stain resistance properties, especially on the most important stains such as fingerprints, skin oil, sweat and cosmetics.
Obtaining the desired performance of high water and oil contact angles and low sliding angles required chemical modification of a linear perfluoropolyether. Four alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether adducts were synthesized, as shown in Figure 1.


As can be seen in Table 1, high water and oil (n-hexadecane) contact angles were observed in all cases. The simpler alkoxysilyl group in [I] and [III] gave slightly higher static contact angles and slightly lower sliding angles for both water and n-hexadecane when compared with [II] and [IV]. The organic linking group between the Si and the perfluoropolyether backbone also had a slight impact on the results, with the amide-containing group [III/IV] giving lower water contact angles and high n-hexadecane contact angles. The results suggest that highly organized molecular arrangement of the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyethers can be achieved on this surface. In all cases the degree of surface hysteresis is small, as shown by the very low sliding angles.

No clear trend was seen for the water and n-hexadecane contact angles although the data did suggest that as the perfluoropolyether molecular weight increased, the sliding angle for water also increased. For the n-hexadecane sliding angle there was no observable relationship with polymer molecular weight.




As can be seen from Figure 4 there is a significant difference in the resistance to rubbing as measured by water contact angle. After 5000 cycles the commercial C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3 material has an 8° reduction in water contact angle, while the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyether shows only a 1° change. The decrease in contact angle of the C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3 material takes effect before 1000 rubbing cycles, and is then constant at 103° for the balance of the test period.

Conclusion
A series of alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyethers has been synthesized and the impact of perfluoropolyether molecular weight, application method and coating durability (by UV irradiation and rubbing) was evaluated. The impact of application method on performance shows a significant effect with the adducts studied. In all cases, large static contact angles were observed in combination with very low sliding angles. The stay-clean and easy-to-clean performance are predicted to be superior for the alkoxysilyl perfluoropolyethers as compared to the current C8F17(CH2)2Si(OMe)3 coatings. Anti-staining and the durability performance make this new technology particularly useful in applications where touch by skin regularly occurs. Specific interest lies in applications such as automotive interiors, kitchen appliances, optical lenses, and electronic displays.This paper was presented at the 11th Annual Coatings for Plastics Symposium, Chicago, IL, April, 2008.
For information about Dow Corning’s fluorosilicone coatings, contact Steve Block at steve.block@dowcorning.com or visit www.dowcorning.com/coatings.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






