Effect of Different Surfactants on Emulsion Polymerization of a Vinyl-Acrylic Latex, Part Three

Davizro / iStock / Getty Images Plus, via Getty Images.
In the two previous columns of “Formulating with Mike,” we covered some of the basics of making alkylphenol ethoxylate (APE)-free vinyl acrylic emulsions and the testing of these emulsions against APE-containing emulsions to show that APE-free versions can have similar performance. In this month’s column, we will make paints with these emulsions, test them, and discuss some of the conclusions from this study. From previous articles, here are the emulsions we made:
Materials and Methods
Surfactants, Vinyl-Acrylic Emulsions, and Paint Formulation
The surfactants used in the study and their main properties are summarized in Table 1.
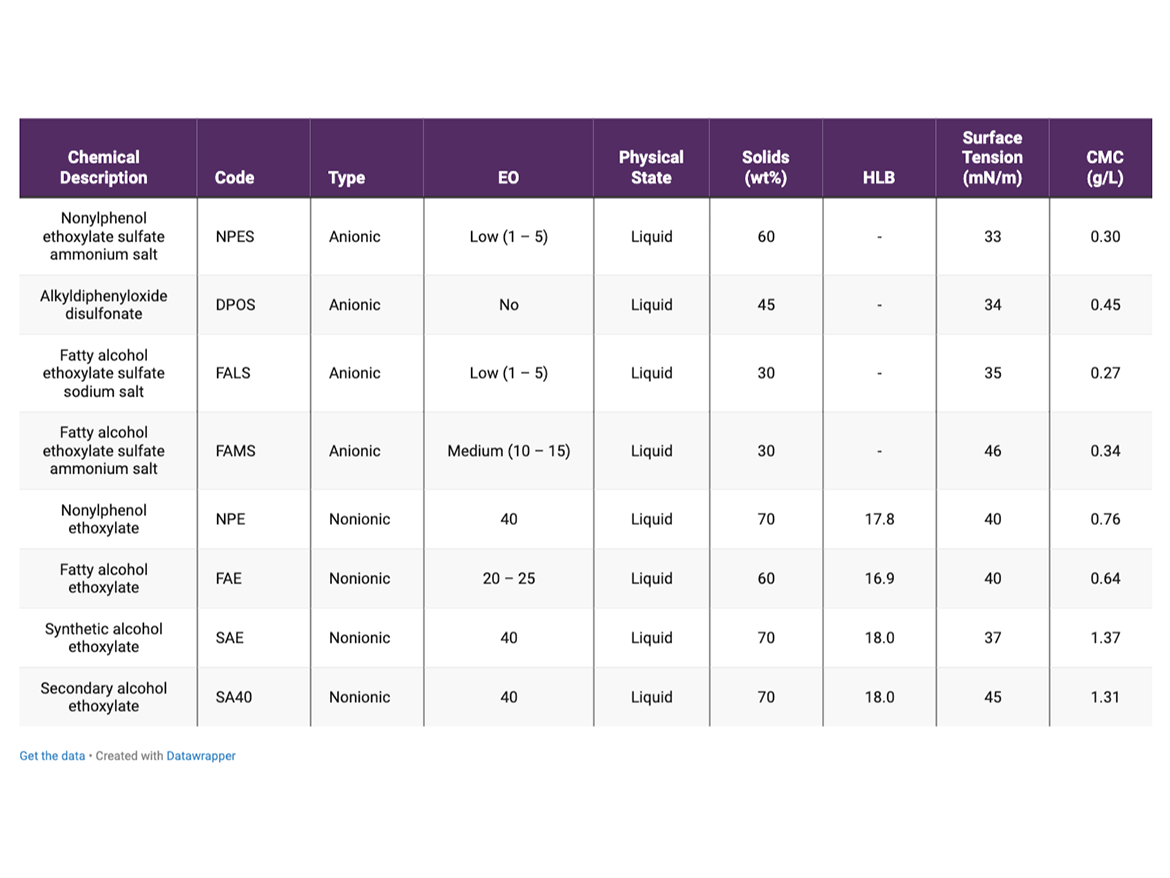
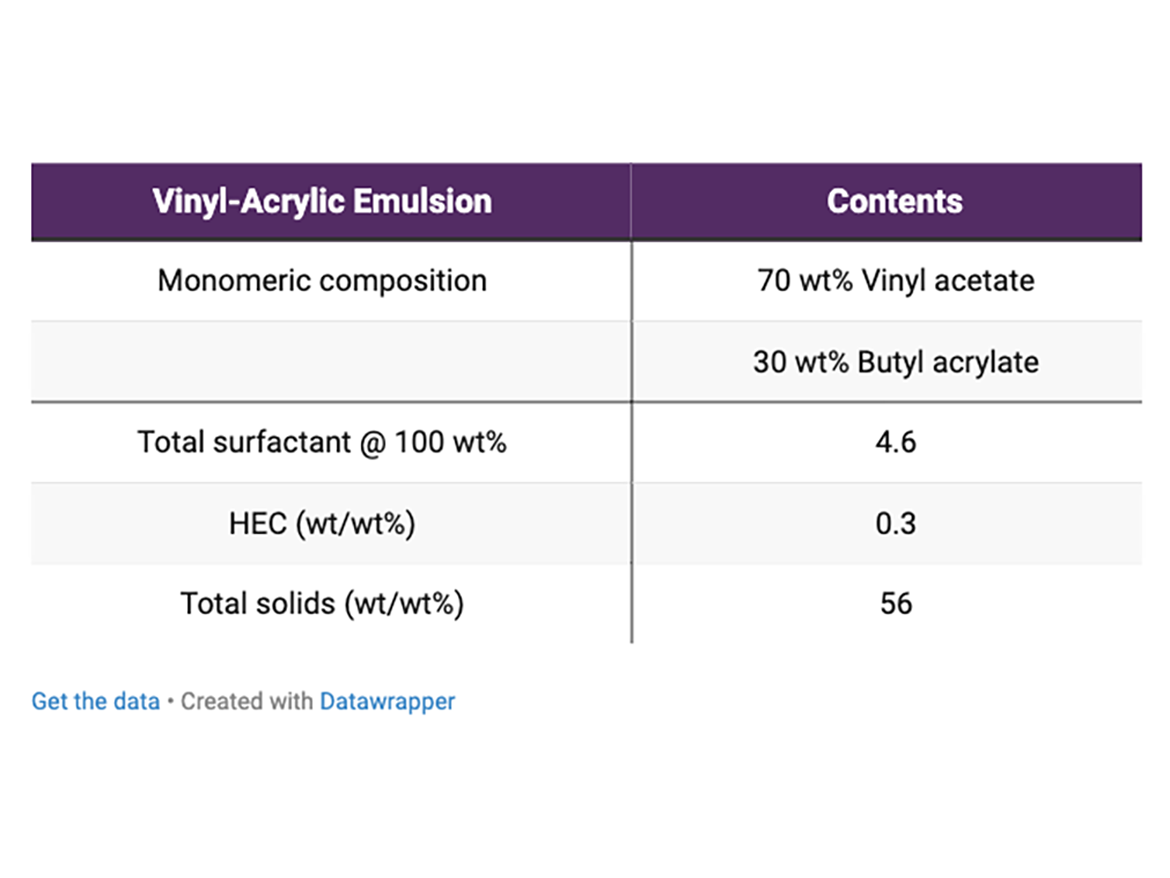
Table 2 contains the general formula for the vinyl-acrylic emulsion. The monomeric composition was chosen to generate latex with calculated Tg about 1 °C so it would require minimum coalescent, and due to this, allow the development of paint formulations with VOC content lower than 50 g/L. The emulsions were synthesized in a 3-L reactor following a semi-continuous process under starve feed conditions.
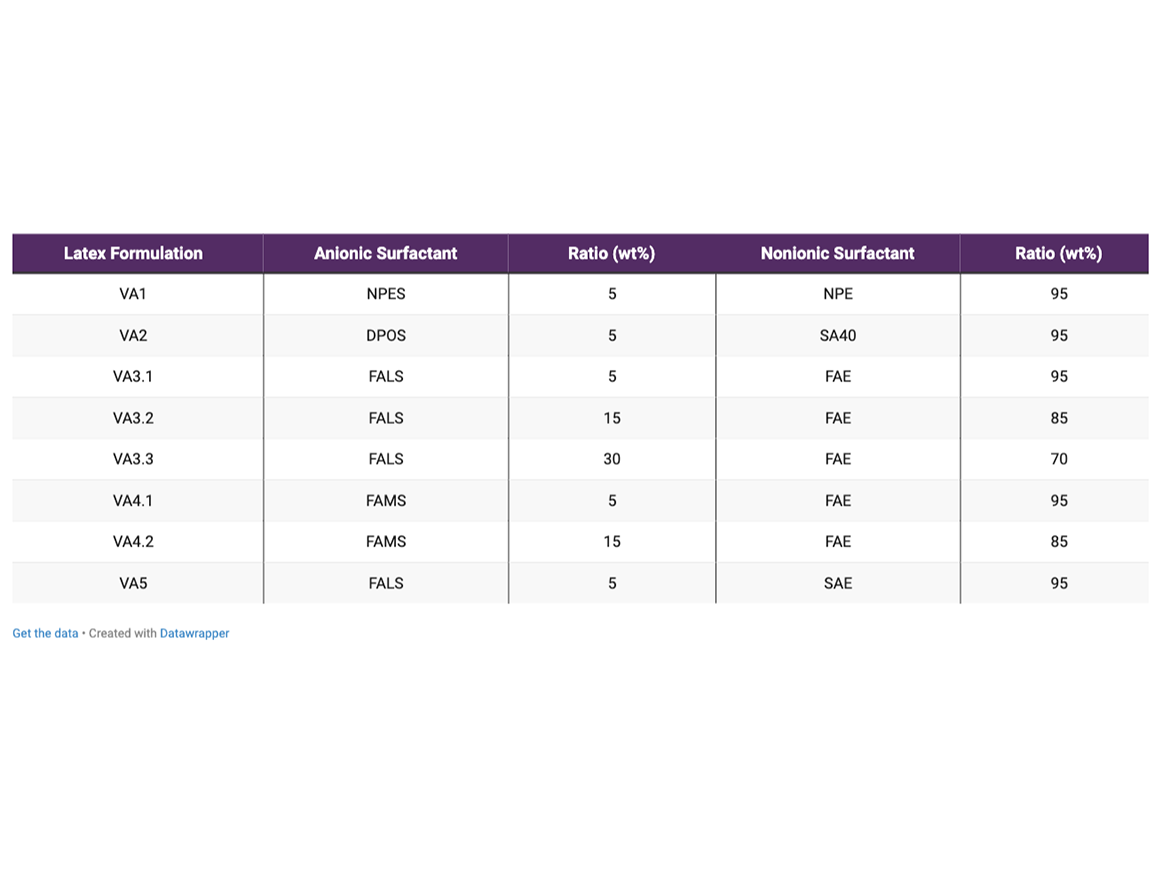
The compositions, processes, and raw materials used in this study were not changed during the assays. The only difference between the formulations is the type of surfactants used and the ratio between anionic to nonionic surfactant. Table 3 contains the different surfactant compositions used in the study and the code for each formulation.
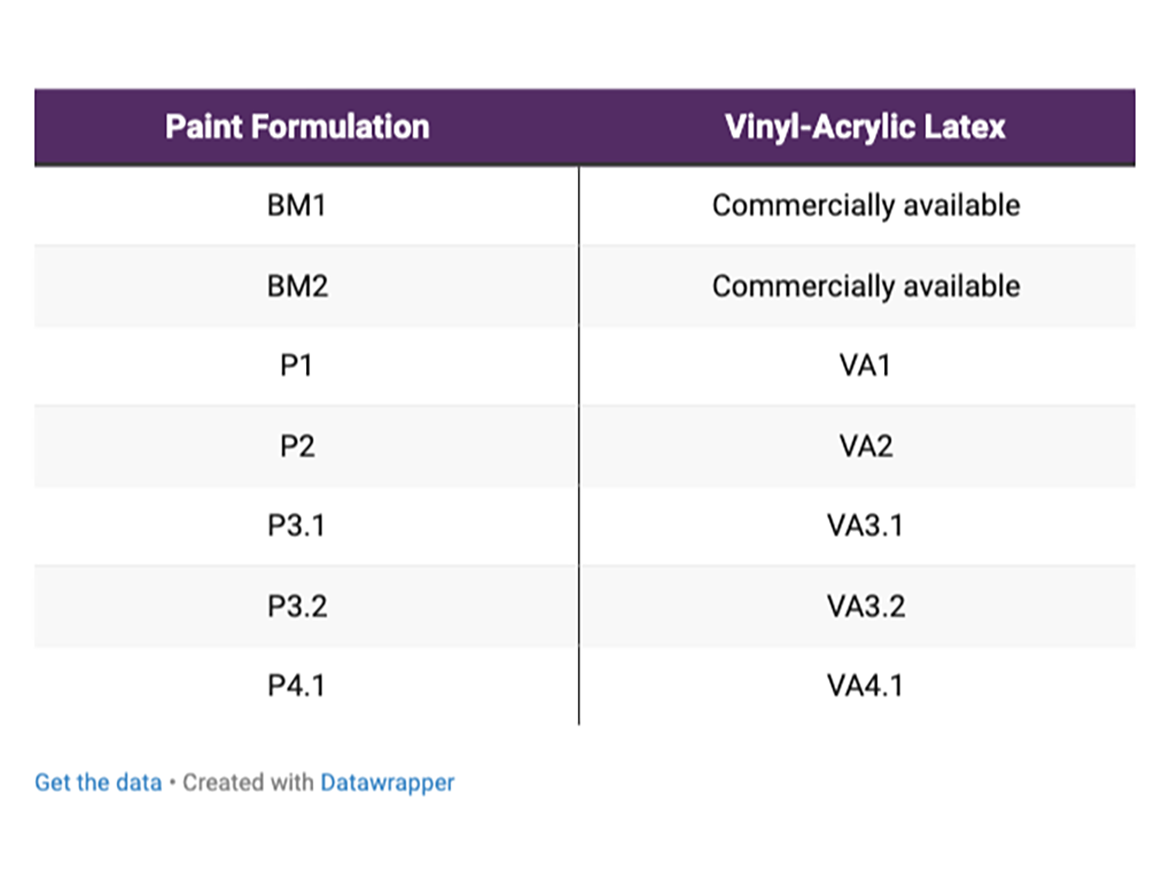
For the paint evaluation, five of the latexes synthesized were selected, and two benchmarks were chosen. The benchmarks represent an APE-based and an APE-free latex. Table 4 contains the codes for the paint formulation according to the vinyl-acrylic latex used in each one.
Vinyl-Acrylic Paint Characterization
Table 5 contains the main results of the vinyl-acrylic paint characterization, and the following sections contain the discussion about some properties affected by the surfactant package selection.
Scrub Resistance
The wet scrub resistance is one of the main tests for architectural coatings, and the quality of the polymer is a cornerstone for a durable formulation. Surfactants are known to cause defects in paint films due to their tendency to adsorb in interfaces and their affinity to water, factors that favor the creation of surfactant domains in the surface of the film and that can allow penetration of water through the film, causing film failures or defects like low scrubability, surfactant leaching, film tackiness due to plasticization, and others. Surfactant selection is a key part of the design of emulsion polymers and paints made with them. Figure 1 contains the scrub resistance for some latexes selected from the previous section and for two benchmark latexes.
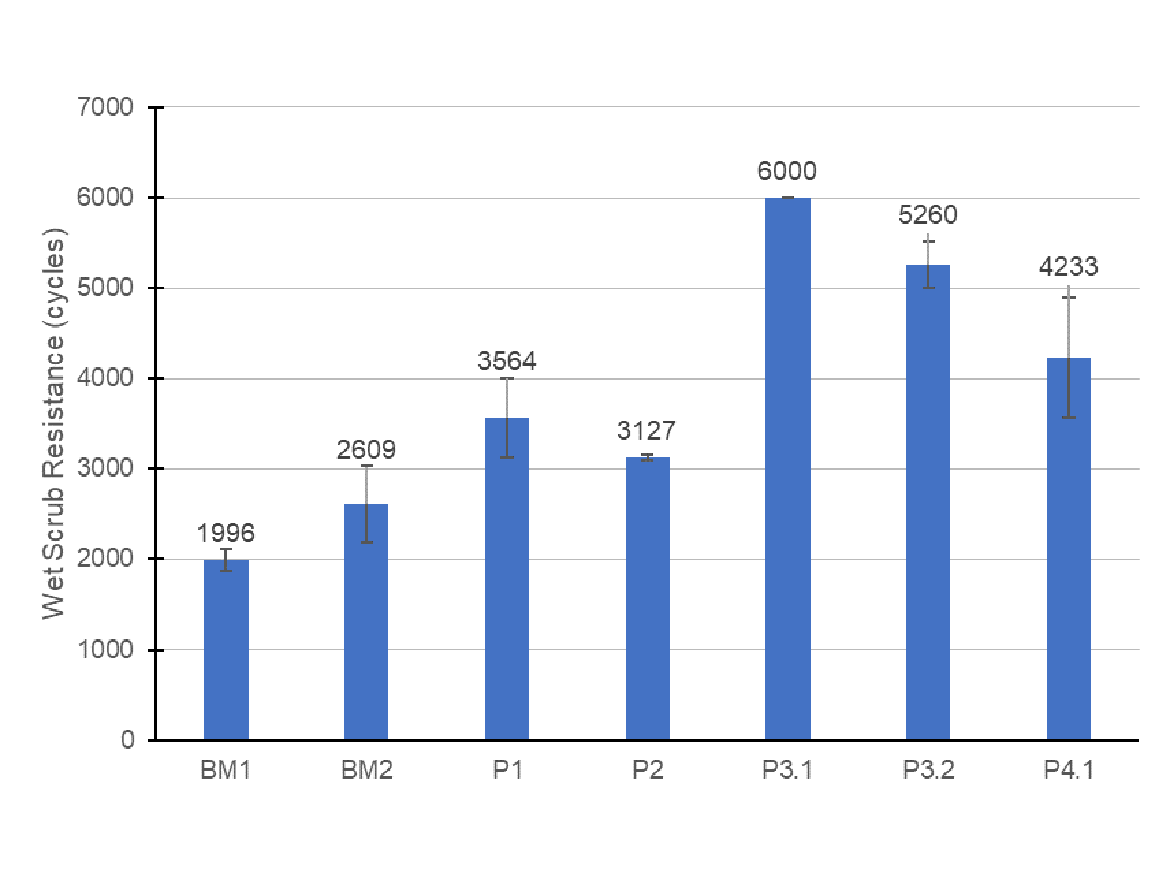
The wet scrub resistance using the benchmark latexes was roughly 2,000 to 2,600 cycles, which showed that the paint formulation chosen was appropriate for high scrub resistance. Replacing it by the latexes VA1 and VA2, the formulations P1 and P2, respectively, also presented high scrub resistance, which showed that the vinyl-acrylic latex formulation was appropriate to generate latexes capable of delivering high scrub.
Interestingly, the latexes VA3.1, VA3.2, and VA4.1 used in the paints P3.1, P3.2, and P4.1, respectively, delivered remarkably high scrub resistance, which could possibly be attributed to a better surfactant distribution in the paint film and higher compatibility of the surfactants with the film, therefore, avoiding surfactant domains to be formed. In addition to that, other effects could cause this higher mechanical resistance of the paint film, like higher molecular weight, better coalescence, and better compatibility of the latex with the paint components. Nevertheless, further studies need to de conducted to evaluate these hypotheses.
Blocking Resistance
The blocking resistance is strongly connected with the structure of the polymer, the hardness of the film, and its coalescence, caused by organic solvents or even by surfactants. Figure 2 contains the blocking resistance for the paints formulated with the latexes synthesized and two benchmarks.

Once again, the benchmarks selected showed that the formulation was appropriate to deliver particularly good blocking resistance, presenting very slight tack even after a short time of application. All the formulations prepared with the latexes synthesized showed the same initial property but with some degree of hardness evolution within time. Except for P3.1, which initially was slightly lower than the others but presented a very good hardness evolution and improvement in blocking resistance. This result showed that the surfactant packages for the emulsions selected were appropriate to generate paints with good blocking resistance, like commercially available paints.
Touchup
The touchup of an architectural coating is especially important to deliver a homogeneous color all over the substrate and to increase productivity for contractors. This property is usually linked to the polymer, even though it can be affected by the other components of the paint like pigments or colorants, dispersant, etc. Figure 3 contains the touchup evaluation for the paints studied.
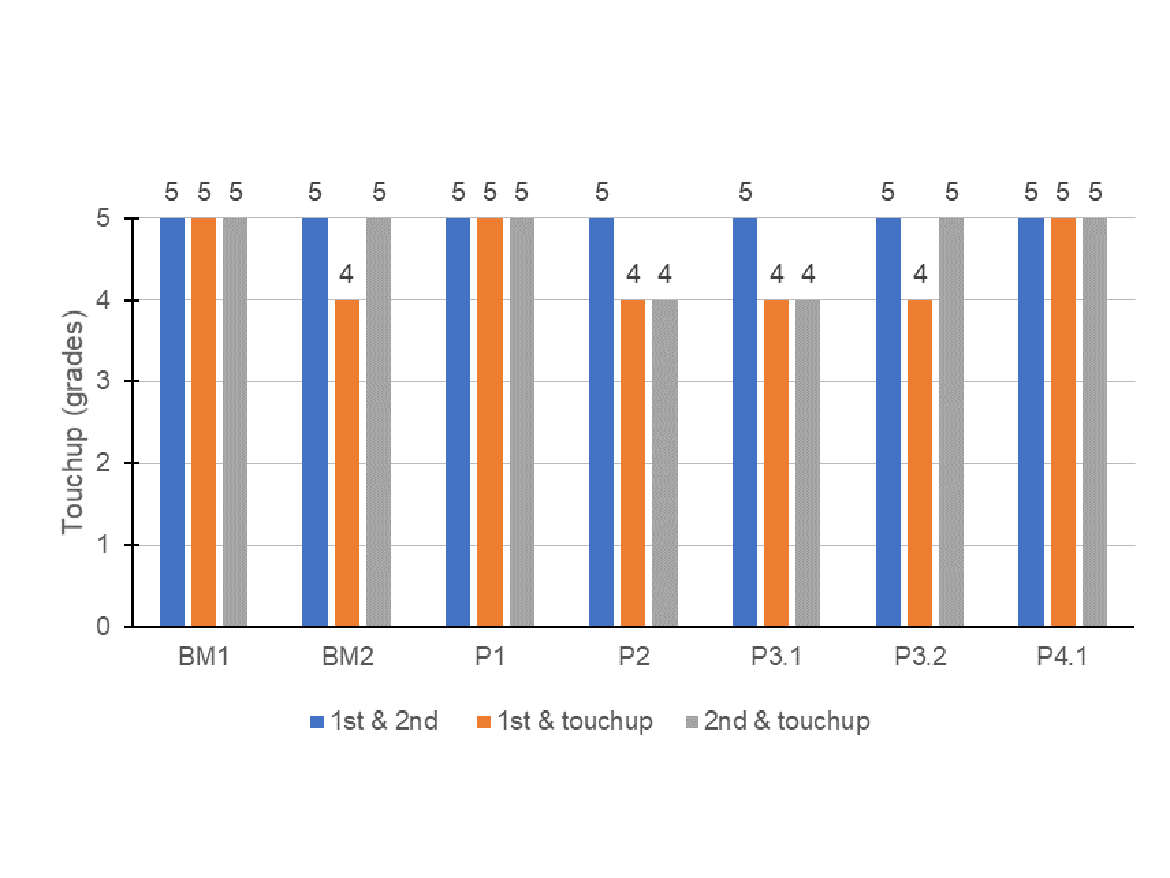
The touchup of the paints formulated with APE-based surfactants, BM1 and P1, delivered a perfect touchup since no color difference was perceivable over the layers. The VA4.1 emulsion, which was used in paint P4.1 was the only APE-free latex evaluated able to achieve the same result. Usually, it is difficult have good touchup with APE-free latexes. All other formulations showed very slight difference in color, which was a good result since there are other ingredients of the paint that can be addressed to improve this requirement.
Conclusion
The goal of the study was to evaluate different surfactants in the emulsion polymerization of vinyl-acrylic latex and understand how the variations in the surfactant’s structure and the ratio of anionic to nonionic surfactant would affect the emulsion and the properties of a paint formulated with it.
In terms of stability, most of the systems generated vinyl-acrylic latexes with acceptable filterable solids, mechanical stability, and electrolytic stability. Some trends were perceived, and they were quite unique because they were related to the nucleation of particles in a vinyl-acrylic latex synthesis. The increase in anionic content in the mix of surfactants reduced the quantity of filterable solids, but it seemed to be balanced by the limited adsorption of the anionic surfactant on latex particles and the increase in the ionic strength of the aqueous phase caused by the non-adsorbed anionic surfactant. The increase of the content of poly(ethylene oxide) in the anionic and nonionic surfactants seemed to reduce the filterable solids, and the proper selection of hydrophobe seemed to improve surfactant adsorption.
Considering the mechanical stability of the latexes, the steric barrier conferred by nonionic surfactants and protective colloids seemed to be more important than the electrostatic repulsion probably because under shear there was desorption of the anionic surfactant and increase of the ionic strength of the aqueous phase. Due to this, the increase in the anionic content in the mix of surfactants did not increase the mechanical stability of the latexes. On the other hand, the increase of the HLB of the nonionic surfactant through the increase of the poly(ethylene oxide) chain conferred a higher mechanical stability. The same trend was observed in a media with high ionic strength.
The particle size of almost all latexes synthesized was below 400 nm, which could be considered acceptable. The results suggested that the low content of poly(ethylene oxide) in the anionic surfactant stabilize less the particles generating latexes with bigger particle size than the anionic surfactant with medium content of poly(ethylene oxide). Additionally, the increase in the poly(ethylene oxide) chain of the nonionic surfactant delivered lower particle size for the systems studied.
The 45% PVC paints formulated with the latexes synthesized were compared against benchmark latexes and the results showed that the surfactants evaluated could produce paints with high quality. The anionic surfactant with low poly(ethylene oxide) chain with the nonionic surfactant with medium poly(ethylene oxide) chain delivered a wet scrub resistance 200% higher than the APE-free benchmark surfactants and 230% higher than the APE-free latex commercially available. On the other hand, the same formulation, but with the anionic surfactant with medium poly(ethylene oxide) chain delivered a perfect touchup, similar to APE-based latexes.
The results of the study showed that changing the surfactant package in the emulsion polymerization can be challenging, but there are alternatives capable of improving properties, such as stability, particle size or final paint quality. Adjusting and fine tuning the emulsion polymerization formula is the key to balancing emulsion properties and final paint quality when changing the emulsifiers package.
All information contained herein is provided "as is" without any warranties, express or implied, and under no circumstances shall the author or Indorama be liable for any damages of any nature whatsoever resulting from the use or reliance upon such information. Nothing contained in this publication should be construed as a license under any intellectual property right of any entity, or as a suggestion, recommendation, or authorization to take any action that would infringe any patent. The term "Indorama" is used herein for convenience only, and refers to Indorama Ventures Oxides LLC, its direct and indirect affiliates, and their employees, officers, and directors.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






