New "Eco-Friendly" Universal Corrosion Inhibitors
In the eighties, due to several environmental scandals, different scientific publications, etc., prompted the need for a new environmentally friendly and transparent chemistry. Conventional coatings contain derived synthetic products from the petrochemical industry that can harm our health and the environment. The danger resides in the heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, mercury, etc., and in VOCs such as xylene, toluene, phenols and formaldehydes, which are emitted by paints and varnishes when applied, or while they dry.
The challenges currently faced by the coatings industry are not just to reduce cost and improve performance but also to fulfill strict legal requirements. In an American technical magazine the technical director of a major national paint company recently reported that his staff spends nearly 40% of its time reformulating their paint in order to meet increasingly stringent VOC regulation. Forty percent of his staff’s time is a lot of time, and is robbing energy and efforts that could be devoted elsewhere, such as toward new developments.
The technical director was expressing a universal phenomenon in the paint industry. Large amounts of manpower are focused on correcting current formulations to new eco-green developments: replacing products containing hexavalent chromium or lead, among other heavy metals, and reducing or eliminating VOCs. This also avoids any undesired labelling that may be associated with toxicity in general.
In terms of corrosion inhibitors, some of the most effective and widely used anticorrosive pigments such as red lead (PbO4), lead silica-chromate (4 (PbCrO4 · PbO) +3 (SiO2 · 4 PbO)), zinc chromate (ZnCrO4), zinc tetraoxychromate (ZnCrO4 · 4 Zn(OH)2), and strontium chromate (SrCrO4), have been and continue to be under heavy scrutiny due to the hazards posed to humans and the environment. Lead compounds are deemed toxic, zinc and strontium chromate are classified as carcinogenic and most recently, according to the EU Directive 004/73/CE, zinc phosphate has been determined to be a danger to the aquatic media.
In general, the latest global trend is to design coatings that comply with the environmental regulations that now exist. These “Eco-Friendly” or “Green” coating systems contain only non-toxic, non-reportable raw materials to ensure no hazard to humans and the environment. The industry has found it very difficult to obtain the same level of performance with the eco-friendly systems as compared to the non-compliant systems.
What is an Eco-Friendly Coating?
Coatings that meet the eco-friendly definition are high- or 100%-solids systems, powder coatings, UV- or EB-curing coatings, low/zero VOC, no heavy metal content, zinc-free or systems that contain no reportable compounds or ingredients in order to meet green label compliant status. Therefore, eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors should not contain heavy metals or non-reportable compounds, and be zinc-free in order to meet the green label compliant standard.
Ever since the use of chromates was restricted, we have been forced to use a variety of different non-toxic corrosion inhibitors specifically designed for a given substrate or resin type in an attempt to match the efficiency and versatility that chrome-based inhibitors offered. But now coatings formulators are demanding today’s non-toxic inhibitors offer as much universal application in a wide range of binders and protective coatings as their toxic counterparts.
What is an Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibitor?
Zinc phosphate (Zn3(PO4)2 · X H2O) was the first and most widely used non-toxic inhibitor for replacing lead- and chrome-based inhibitors. Historically, standard zinc phosphate has demonstrated acceptable performance in real outdoor exposure, but less efficiency compared to chromates in marine environments and in accelerated weathering tests such as salt spray and cyclic corrosion (i.e., Prohesion). However its user-friendly, low cost, universal application, and good package stability in a variety of general-purpose industrial and protective coating applications, made zinc phosphate the most popular choice early on for replacing chrome- and lead-based inhibitors
Today, in order to meet the eco-friendly labelling demands, zinc phosphate and modified zinc-containing inhibitors can no longer be used. This has caused yet another dilemma for the inhibitor suppliers, as the current offering of non-zinc inhibitors on the market have generally shown inferior anti-corrosion performance in accelerated corrosion tests, especially on steel substrates, as compared to most zinc-based inhibitors. Also, current zinc-free inhibitors are very limited in their application scope, performing well in some coatings systems and poorly in others.
Our goal was to develop a zinc-free inhibitor that not only met all the environmental demands required for green label compliant coatings but also provided a high level of cost-effective corrosion resistance, exhibited good correlation in accelerated and real-world environments, and offered universal application similar across a wide variety of resin systems and substrates equivalent to its zinc-based counterparts.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA
|
| Figure 1 Click to enlarge |
Development Process for Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibitors
First we developed our targeted property list to give direction and scope to our experimental design:
- direct anodic inhibitor;
- modified metal phosphate complex;
- universal application – water and solvent systems;
- improve early (accelerated testing) corrosion resistance;
- good correlation between accelerated testing and real world environments;
- good multi-substrate performance;
- user friendly – easy to incorporate;
- application in thin-film (< 25µ d.f.t.) systems;
- good package stability; and
- greater price stability vs. zinc based inhibitors.
We knew this was not going to be an easy task, especially with the limited eco-friendly corrosive inhibitive chemistry available in conjunction with the cost-effective performance targets we set for this product.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 2 Click to enlarge |
We determined if we were going to be successful in meeting our development goals we needed to employ a unique combination of chemical and physical properties.
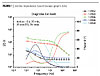
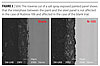
On the chemistry side we evaluated various metal phosphate-based complexes deposited on a variety of inert carriers or core pigments to determine what combinations would provide the best cost-effective, universal application. We also looked at the effect of organic modification on the various inorganic complexes. Standard zinc phosphate and several modified zinc and zinc-free inhibitors were used as controls. The controls and experimental offerings were then initially screened using a combination of surface compositional and structural analysis that included Electro-Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) (Figure 1), SEM/EDX Mapping (Figures 2,3), XRD, and in-house solution potential techniques to determine which complexes provided the most contribution effect.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 3 Click to enlarge |
The respective coating systems were applied to a variety of applicable substrates and to a battery of accelerated corrosion tests that included standard salt spray (ASTM B 117), cyclic QUV/Prohesion testing (ASTM D 5894) (Figure 4), humidity testing and exterior exposure.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 4 Click to enlarge |
On the physical property side we chose to use the key characteristics of our top-performing, modified zinc-based inhibitors. We employed a spherical morphology particle shape, a very fine mean particle size (avg. 1.0 µ) and a narrow particle size distribution range that includes a very controlled percentage of nano particles (Figure 5). Our past research shows that this combination of physical properties provides ease of dispersability, excellent thin-film performance, and optimum pigment packing properties that synergistically enhanced the anti-corrosion performance.
Test Results
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 5 Click to enlarge |
Finally, after screening over 250 experimental offerings and testing over 2,000+ test panels, we found the mixed metal calcium-strontium phosphate complex deposited on a silicate core provided the best overall performance (Appendix, Figure 10-13). We also discovered an organo-modified version of this same complex produced some additional advantages in the area of film formation, adhesion promotion, and substrate wetting (Appendix, Figures 14-18).
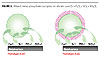
The basic formula for these products is shown in Figure 6. Both experimental prototypes, 301 and 302, provided excellent direct anodic inhibition from the combination of the calcium and strontium cations, but also provided good cathodic inhibition due to the basicity/alkalinity of the silica core. Its basic nature reduces the amount of oxygen needed to passivate the formation of rust.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 6 Click to enlarge |
The organic surface treatment used in prototype 302 showed improved mechanical properties in terms of better wetting in organic systems without decreasing its performance in waterborne systems, reduced pigment – binder interface, which makes the flow of water and electrolytes through the organic coating difficult and at the same time protects the pigment making it more inert when reactive resins or those with high acid values are used.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Table 1 Click to enlarge |
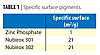
The pigment’s chemical activity is a result of the active chemical substance’s solubility (270 mg/L). Its small particles provide easier solubility due to greater specific surface (Table 1), which is one of the keys to its anti-corrosive effectiveness.
At the same time, the organic surface treatment facilitates the dispersion of active nano-particles within the system. The photographs in Figure 7 show the difference in agglomeration between both pigments.
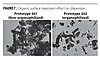 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 7 Click to enlarge |
A strong contribution margin was also obtained due to the unique particle morphology and high aspect ratio of the fine, narrow particle size distribution (Figure 8).
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 8 Click to enlarge |
Good package stability was seen in all systems tested with Prototype 301 and 302. We were especially encouraged with the compatibility of both prototypes in high reactive systems such as acid catalyzed and 2K polyurethanes where it provided good cost-effective performance without affecting the pot-life or cure properties of these systems. Figure 9 shows the good stability in terms of viscosity change over time as compared to the same system containing standard zinc phosphate.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 9 Click to enlarge |
Summary
To sum up, based on our project design and extensive validation testing, we found experimental prototypes 301 and 302 to provide the best overall universal anti-corrosion performance of all the zinc-free offerings. These uniquely designed calcium-strontium mixed metal phosphate complexes provided comparable, and in some cases, improved cost-effective performance over standard zinc phosphate and the modified zinc and zinc-free inhibitors they were compared against. The zinc-free chemistry of prototypes 301 and 302 also provided good package stability in a variety of resin systems, including high acid value, acid catalyzed, and 2K urethanes.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 10-13 Click to enlarge |
Overall we feel experimental prototypes 301 and 302 meet the performance, cost, and most importantly, the environmental requirements for a universal, eco-friendly, zinc-free inhibitor.
 Credit: Nubiola USA Credit: Nubiola USA |
| Figure 14-18 Click to enlarge |
Appendix
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






