New Additives for Radiation-Curable Systems
Radiation curing, an innovative and rapidly growing technology, is used in markets such as graphic arts (including overprint varnishes and inks), coatings (including wood and general industrial coatings), and adhesives and electronics. The technology is mainly characterized by its instant curing within seconds or even less, which permits high rates of production. In addition to high productivity, other benefits of the process include space saving, waste reduction and low-temperature treatment. Moreover, radiation curing is associated with ecological benefits such as low emissions and energy consumption.
The development of radiation-curable coating formulations is advancing rapidly, with significant performance improvements in recent years. Radiation-curable coatings can be applied to a large number of materials and exhibit good adhesion properties on various substrates (displaying a high degree of surface hardness and gloss). In terms of realizing more eco-friendly products, the development of solvent-free formulations has been widely promoted. This fast-moving development results in many new challenges and requirements with respect to radiation-curable compositions. In many cases, the use of additives helps to overcome technical problems and improve or fine-tune the properties of the final coating.
Additives Improve Coatings
The additive function is very specific in nature and provides a coating with a range of properties. Wetting and dispersing additives, for example, enhance uniform pigment distribution, rheology additives improve flow behavior of the coating formulation, and defoaming agents prevent the inclusion of air bubbles. The final surface properties, such as slipperiness, recoatability, ease of cleaning and leveling, are strongly influenced by the surface-active additives. These additives segregate toward the coating/air interface and tailor the surface properties. The performance and properties that these additives attribute to the coating depend on their chemical composition and their structure.
New Additives forRadiation-Curable Systems
In order to meet the new challenges faced by radiation-curable technology, there is a need for new additives that provide satisfying properties. Requirements might range from anti-slip/no slip to high slip, or from anti-adhesion (easy-to-clean properties) to good adhesion properties (improved recoatability). With respect to the rapid hardening of radiation-curable coatings, surface-active additives need to effectively orient toward the coating/air interface.
In this article, we present a series of crosslinkable, surface-active additives for radiation-curable systems that have been designed to tailor surface properties precisely within a wide range that meets the specific needs of the end user. When developing additives, a few important parameters need to be considered.
Chemical Composition
An important component of surface-active additives is polydimethylsiloxane. Polydimethylsiloxanes are incompatible with nearly all organic materials and have a strong tendency to segregate to the coating/air interface. As pure polydimethylsiloxanes show many drawbacks in the applied coating, they have to be organically modified with binder-compatible moieties in order to improve their compatibility with a broad range of polymeric binder formulations. The well-balanced mix of the polysiloxane and the different modifications determine the compatibility and effectiveness of the obtained additive within different coating systems.
Polymeric Architecture
The structure of the surface-active additive is of great importance. It strongly influences its effectiveness and segregation behavior. Common polymeric architectures are linear ABA-structured copolymers or branched comb-shaped copolymers. With the application of new technologies such as macromer technology, other structures such as AB-structured block copolymers become possible. Highly branched or hyperbranched polymers also present advantages in terms of their segregation behavior. Moreover, in comparison to their linear counterparts, they possess a multitude of end groups that can be functionalized.
Using a versatile toolbox of chemistries and technologies, four different additives with properties adjusted for specific applications have been designed (Figure 1).
Additive A (BYK-UV 3535) is a siloxane-free additive. It is based on a hydrophilic polyether that has a hyperbranched structure, which enhances the segregation to the coating/air interface. As for the polysiloxane-based additives, Additives B, C and D (BYK-UV 3576, BYK-UV 3575 and BYK-UV 3505 respectively), the polysiloxane content was varied from low to high. The activity of the polysiloxane-based additives depends not only on their molecular weight but also on their molecular architecture. Additives B and C possess a similar molecular architecture and can be characterized by a linear ABA structure, with the main difference being their siloxane content. The ABA structure can be functionalized at both ends of the molecule.
Additive D is based on polysiloxane macromer technology, meaning it can be functionalized at only one end of the molecule. Additive D possesses a molecular architecture that can be characterized by an AB structure. The polysiloxane parts of the B, C and D additives were first modified with suitable polyether/polyester moieties to render them compatible in the various formulations, and their end group(s) were then functionalized with a multitude of UV-reactive groups. Up to four UV-reactive groups ensure the crosslinking of the additives into the binder matrix, which prevents migration and allows the additives to be fixed permanently to the surface, guaranteeing long-lasting effects. This is especially desirable when slip and easy-to-clean/anti-graffiti effects are the goals.
It is worth adding that a mild process technology was chosen for production of the new additives. This has advantages over conventional acrylation technologies and has led to the manufacture of colorless and odorless products. Application results showing the properties that can be achieved by using the additives are described below.
Compatibility
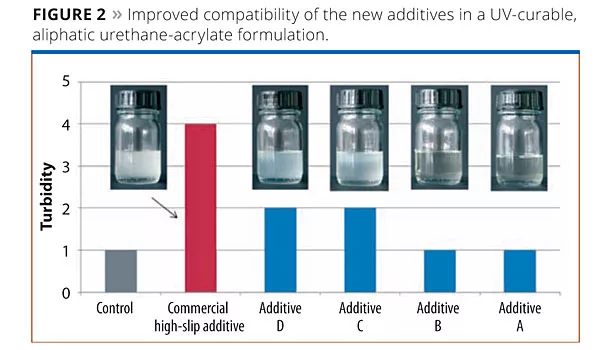
Polysiloxane-based additives, especially additives with a higher content of polysiloxane, are used to strongly reduce surface tension or to provide slip and mar resistance as well as easy-to-clean properties to the coating. A drawback of these additives is that they are often incompatible with the coating formulation and cause turbidity. At high dosage, they often cause problems with adhesion to the substrate. The meticulous design of the structure and composition of the new additives, especially in the case of Additives C and D, has resulted in exceptionally good compatibility of the additives with the coating system with no loss of performance. To achieve this, the additives were incorporated in an aliphatic urethane acrylate formulation (0.3% dosage) and compared to a commercially available high-slip additive used as a benchmark. The turbidity was judged visually (1 = clear; 5 = very turbid). Results are depicted in Figure 2.
The improved compatibility was achieved by carefully adjusting the polarity of the modifications and arranging them within the core of the polymer architecture.
Effect on Surface Tension
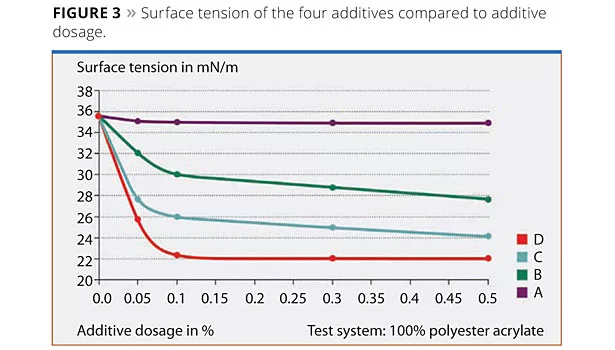
A significant parameter affecting the quality of the final coating is the surface tension – more specifically, the surface tension differences of the materials involved or the differences within the applied coating that may occur from solvent or water evaporation, crosslinking of the binder (monomer/oligomer combinations) or external sources such as dust particles. Upon application or drying of the coating, this may lead to poor substrate wetting, crater formation, formation of Bénard cells or bad leveling. These defects degrade the optical appearance of the coating and its ability to protect the substrate. Using the new additives, the surface tension can be properly adjusted to the required value. To bring this about, the additives were incorporated in four different concentrations in a 100% polyester-acrylate system. The surface tensions of the liquid coating formulations were measured with a KRUSS Processor Tensiometer using the du Noüy ring method. Figure 3 shows the surface tension of the liquid formulation with respect to the additive dosage of the four additives.
Additive A, which is polysiloxane-free, does not affect the surface tension over the whole dosage range. The effectiveness of the polysiloxane-containing additives increases with increasing polysiloxane content. Additive D, based on polysiloxane macromer technology and containing the highest amount of polysiloxane, is extremely effective and already reduces surface tension significantly at a very low dosage of 0.1%. All the products eliminate surface tension differences and lead to improved leveling of the obtained coating.
Effect on Surface Slip
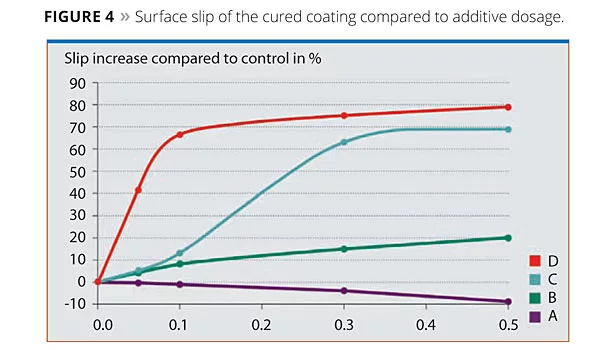
In many cases, applications require coatings to have improved surface slip properties. Certainly, surfaces with high surface slip are more scratch and mar resistant, more resistant to blocking and less prone to soiling. It might also be necessary to adjust the surface slip to a particular level. For example, the surface slip of the overprint varnish of magazines should not be too high; otherwise the magazines cannot be easily stacked. For parquet floors, it is desirable to reduce the surface slip as much as possible to prevent people from falling. To this end, the same polyester acrylate formulations that had been used to measure the surface tension were applied to glass substrates and cured with a mercury vapor lamp (120 W/cm, belt speed 5 m/min). The force required to move a slider horizontally across the surface was measured, giving coefficient of friction values that were used to assess the slip of the surface. From the reduction in the coefficient of friction, the slip increase compared to the control was calculated as a percentage. Negative values indicated the anti-slip effect. Results are depicted in Figure 4.
As expected, the polysiloxane-based surface additives show an increase in surface slip and the performance is dependent on the polysiloxane content. Additive B, which contains a low amount of polysiloxane, only has a moderate impact on surface slip. With Additive C, the increase in surface slip is dependent on the dosage. At low dosage it behaves similarly to Additive B, and at higher dosage it drastically increases the surface slip. Additive D, the additive based on polysiloxane macromer technology, is extremely effective. Already at a low dosage of 0.1%, it increases surface slip by about 70%. This is due to the high silicone content and a highly mobile structure that can readily orientate to the coating/air interface. By contrast, the polysiloxane-free Additive A, which has no influence on the surface tension, leads to a reduction in surface slip compared to the control. At higher dosage, it gives rise to anti-slip effects. This can be explained by its polar polyether structure.
Effect on Surface Energy of the Coating and its Easy-to-Clean Properties
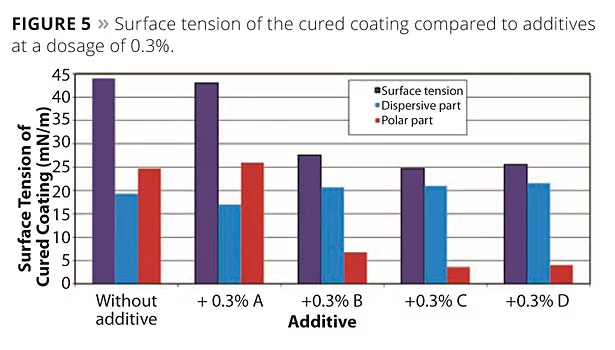
An important characteristic with respect to recoatability and easy-to-clean properties is the surface energy of the cured coating and, more specifically, the polar and dispersive portion of the surface energy. A high-polar portion generally implicates improved recoatability, while a low-polar portion prevents the coating from soiling. The surface energy of the cured coatings with an additive dosage of 0.3% is determined by using a contact angle goniometer. By measuring the contact angle of different liquids of known surface energy, the surface energy of the cured coating with its polar and dispersive portions is calculated by application of the Owens, Wendt, Rabel and Kaelble method. Results are depicted in Figure 5.
Polysiloxane-free Additive A causes a slight increase in the polar part and a reduction in the dispersive portion of the surface energy. This result is in line with the anti-slip effect that is observed in Figure 4. Moreover, the recoatability properties of the polyester acrylate coating containing Additive A are improved. To achieve this, a waterborne polyurethane acrylate dispersion was applied on top of the polyester acrylate coating containing Additive A. The cross-cut test clearly showed an improvement in the intercoat adhesion compared to the coating without any additive.
The polysiloxane-based additives lead to a distinct decrease in the total surface energy. This decrease is completely at the expense of the polar part. In the case of Additives C and D, which have the highest polysiloxane content, the polar part of the total surface is reduced significantly. Low values of the polar part of the surface energy are in line with the slip values shown in Figure 4 and indicate that easy-to-clean properties can be obtained. In fact, with both additives, the coatings showed good easy-to-clean properties (marker test) and oil repellency. It must be noted that, in the case of the very active Additive D, the easy-to-clean properties are already obtained at low dosage of 0.3%.
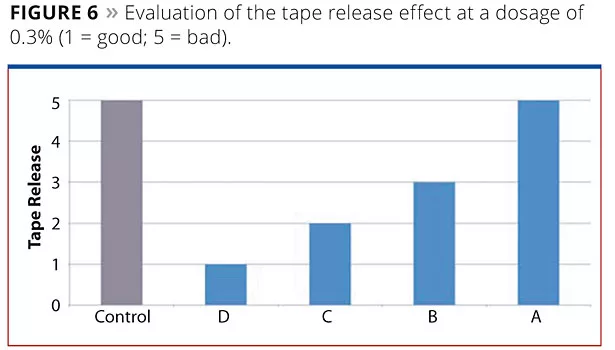
Tape Release
In certain applications, especially in furniture coatings, tape release is desirable. It should be possible to remove adhesive tapes and all kind of stickers easily from a surface without leaving traces or damaging the latter. Polysiloxane-based additives are generally suitable to improve the release effect. In Figure 6, an evaluation of the four additives is shown (1 = good; 5 = bad). The relationship between polysiloxane content and tape release is observable. Additive D, which has the highest polysiloxane content, exhibits the best tape release effect. With decreasing polysiloxane content, the effect decreases. Additive A, which is polysiloxane-free, does not provide any release effect.
Conclusion
A family of new radiation-curable additives with an improved compatibility in various formulations (solvent-free, solvent and waterborne) and covering a broad slip range has been developed. A versatile chemistry and a modular molecular approach have made it possible to adjust the additive properties – from anti-slip/no-slip to high slip, from recoatability to tape release and ease of cleaning, and to improve the leveling. Moreover, the new additives are colorless, odorless, present an improved compatibility in a broad range of formulations and are crosslinkable in EB- and UV-curable systems.
This article originally appeared in the Radtech Report, Issue 3, 2013.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!




